why did my dog get kidney failure
10 Common Causes of Kidney Disease in Dogs

Kidney disease is a common problem of older dogs, affecting an estimated 10% of canines in their lifetimes1. There are a number of causes that may affect different age groups and have different consequences, ultimately though, chronic kidney disease (occurs over time) or acute kidney injury(occurs suddenly) will always have the same resultone sick pup. The signs of illness in your dog reflect the failure of the kidneys to do their many jobs well enough.Learn the basics of chronic kidney disease in dogs.Below you will find a brief description of ten common causes of kidney disease. These are the targets of your veterinarians testing:1. Damage to the kidney filters (glomerular disease)The glomerulus of the kidney (kidney filtration mechanism) is commonly involved in canine kidney disease. Early on, we expect no signs of illness, but since glomerular disease may be caused by infections (like Lyme disease) or cancer, amongst other things, time can make the problems worse. Over time, inflammation, in the glomerulus of the kidney, damages the surrounding kidney tissues, creating the chronic kidney disease that makes your dog feel sick.
Learn more about glomerular disease in dogs.
2. Infection of kidney tissues (pyelonephritis)Infection of kidney tissues with bacteria, or rarely, fungal organisms, is one of the kidney diseases that may have a more favorable outcome, so your veterinarian will be on the lookout for it. Our goal with pyelonephritis is to kill the bacteria that can cause the damaging inflammation. This should limit progression of any chronic kidney disease or assist with recovery from an acute kidney injury. A bacterial urine culture and susceptibility can verify the infection and identify which antibiotic might work the best.3. Kidney stones (nephrolithiasis)Kidney stones can be the product of chronic bacterial infection, genetics or diseases that alter blood or urine characteristics. Nephro (kidney) liths (stones) dont seem to cause dogs much pain, but this can change if they cause blockage within the kidney or its collecting ducts; it can also change if they contribute to infection (see pyelonephritis).
Learn more about kidney stones in dogs.4. Kidney blockage (ureteral obstruction with hydronephrosis)Kidney stones can fragment and be carried along with urine into the ureter, the long narrow tube that connects each kidney to the urinary bladder. They are probably painful during their transit, but the bigger concern is the consequence to the kidney if they become lodged there, causing partial or complete blockage. New urine cannot exit the kidney easily and it backs up, causing the kidneys to swell. With enough pressure, the kidneys enlarge (hydronephrosis) and become damaged. If both ureters obstruct at the same time, it can prove disastrous.
5. Damage to kidney tubules (tubulointerstitial disease)Inflammation and damage to the kidney tubules and supporting tissues commonly leads to chronic kidney disease. In many cases there is no identified cause, and thus no option for specific treatment. This type of kidney disease can only be confirmed by microscopic examination of a kidney biopsy specimen, but biopsies are not usually recommended.6. Bacterial infection (leptospirosis)Bacterial infection with leptospires causes kidney disease and other organ challenges in dogs and people all over the world. Normally, the effects of leptospirosis will be quite sudden and cause an acute kidney injury. Occasionally, the infection might cause chronic kidney disease. Quick recognition of this highly treatable disease should lead to a better outcome and protect your dogs friends and family (YOU!) from becoming infected by contact with urine or other body fluids.
Learn more about leptospirosis in dogs.
7. ToxinsLots of household items can damage the kidneys, not just antifreeze. Ordinary table foods like grapes and raisins; certain commercial jerky treat products; common OTC medications like aspirin or other nonsteroidals (NSAIDs); or prescribed medications can all cause kidney disease. Venoms, pesticides and heavy metals are less common toxins. We know dogs like to lick stuff, eat stuff, roll in stuff or bathe in stuff, but that can put them at real risk. To reduce your buddys risk of kidney injury, consider limiting his free-roaming behaviors and refrain from giving him any medications without discussing it first with your veterinarian.
See the top 5 most damaging kidney toxins for dogs.
If you have any reason to believe your dog has been poisoned, contact your veterinarian or an emergency veterinarian right away. You may also contact:
8. CancerFortunately, kidney cancer is not very common in dogs. Unfortunately, treatment options for kidney cancer are rather limited. Solitary tumors affecting only one kidney can be removed by surgery with a good outcome, if the cancer is benign or has not spread to other parts of the body (including the opposite kidney). Your dog only needs one good kidney to function normally. If the cancer is more widespread, as usually occurs with lymphosarcoma, surgery will not be an option for cure. Microscopic analysis of a biopsy or small needle sample is needed for the correct diagnosis of cancer and appropriate treatment plans.
Learn 10 signs of cancer in dogs.
9. Protein issue (amyloidosis)Patients with amyloidosis lose function in certain organs, including the kidneys, because protein deposits replace the normal tissue. It is an uncommon consequence of chronic inflammation affecting other parts of the body. It may also be genetically programmed in some dog breeds. Amyloid deposits cannot be cleared away, and the functional kidney tissue that is lost cannot be replaced, so the prognosis is not good.
Learn more about amyloidosis in dogs.
10. Hereditary There are genetic links to various kinds of kidney disease for many purebred dogs. Some young dogs fail to develop normal kidneys, or have kidneys that are large and grape-like, with many fluid- filled cysts. These dogs show signs of kidney disease as youngsters. Other dogs with congenital problems of the glomerulus or with a predisposition to amyloidosis might only show signs or symptoms of kidney disease when theyre adults.
If you have any questions or concerns, you should always visit or call your veterinarian -- they are your best resource to ensure the health and well-being of your pets.References:
- Brown SA. Renal dysfunction in small animals. The Merck Veterinary Manual website. Updated October 2013. Accessed January 14, 2015.
Kidney Failure in Dogs: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
In this post, well dive into the causes of kidney failure in dogs, common symptoms you should look out for, available treatment options, and more.
Table of Contents
Pro Tip: Not all pet insurance will cover your vet bills if your dog develops a long-term illness. Thats why its very important to have the right pet insurance plan in place.
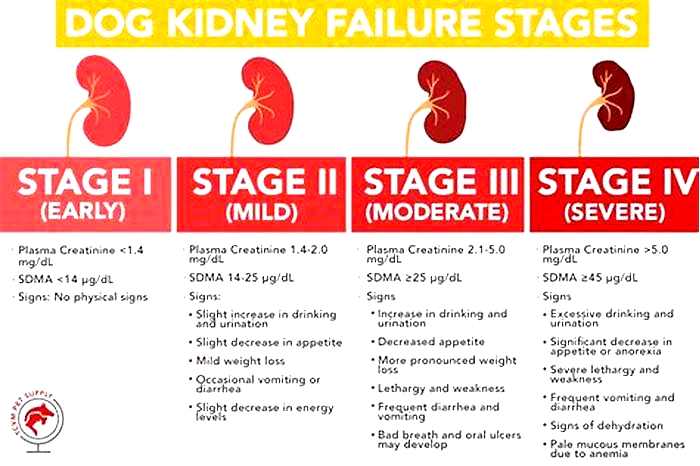
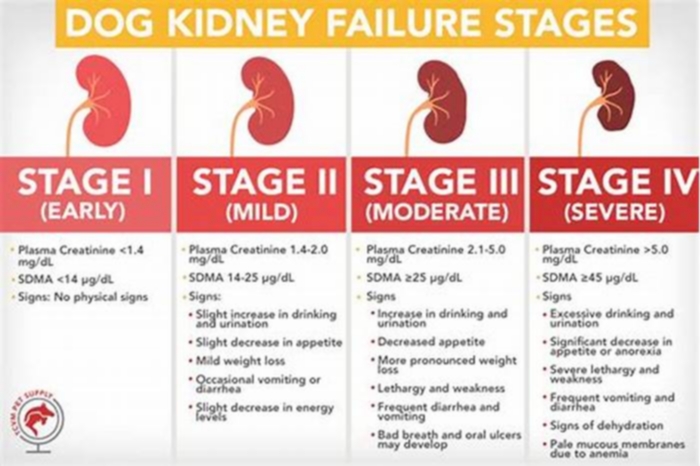
Types of kidney failure in dogs
Just like in humans, healthy kidneys in dogs control blood pressure, regulate hydration, remove toxins, release hormones needed to produce red blood cells, and maintain a normal electrolyte balance. If the kidney function is impaired, kidney failure occurs. When the kidneys dont work properly, a number of other organs can be affected, including the brain and heart.
Kidney failure (also called renal failure) in dogs can be chronic or acute:
Chronic kidney failure
This occurs when the kidneys lose function gradually and is typically caused by degeneration related to old age. Chronic kidney failure is the most common type of kidney disease in dogs, occurring in 0.5% to 1% of dogs.
Acute kidney failure
This occurs when a canine's kidney function suddenly decreases, usually within hours or a few days. Its typically caused by a severe kidney infection or the consumption of toxins.
The main difference between these two types of kidney failure is that acute kidney failure can be reversed with timely and aggressive treatment. Chronic kidney failure, on the other hand, cant be reversed or cured and it can only be managed. In most cases, the damage to the kidneys has been happening for more than three months and the kidneys will continue to worsen.
What causes kidney failure in dogs?
Chronic kidney failure in dogs
The exact cause of chronic kidney failure is often difficult to pinpoint because of its slow onset. Early symptoms are usually mild and can be easily overlooked or dismissed.
Dental disease is a leading cause of chronic renal failure in senior dogs. Bacteria build up in the animals teeth and enter the digestive system through eating and drinking, affecting the kidneys ability to filter waste over time.
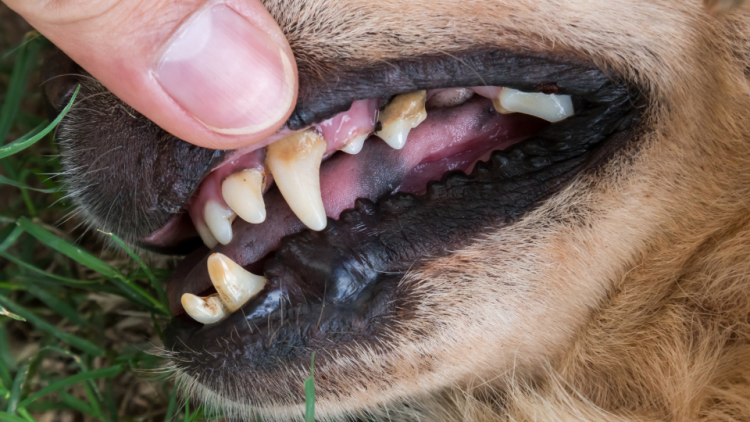
Chronic kidney failure can also be caused by:
- Congenital diseases or birth defects (such as agenesis, when the dog is born missing one or both kidneys)
- Kidney cancer (renal neoplasia)
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Kidney infections
- Fanconi syndrome
- Elevated calcium (hypercalcemia)
- Kidney stones
- Renal dysplasia
- Immune system dysfunction
- Poor blood flow to the kidneys
- Blocked urine movement or flow
- Certain medications (such as NSAIDs and some antibiotics)
Acute renal failure can also lead to chronic renal failure.
Acute kidney failure in dogs
Acute renal failure is most often a result of a dog ingesting poison. It might be antifreeze, household cleaners, or certain drugs. Some human foods like grapes and raisins have also been known to cause kidney failure if eaten frequently and in larger quantities.
Severe bacterial infections can also cause acute kidney failure. Even though kidney infections can occur spontaneously, theres usually a reason why the dog has trouble fighting off the infection, such as urine blockage or kidney stones.
Leptospirosis is one example of a bacterial infection that can cause sudden renal failure in pups. Our canine companions can get leptospirosis by coming into contact with infected urine, water, soil, water, food or bedding, or through a bite from an infected animal. Be sure to talk to your vet about vaccinating against this disease.
Kidney issues can also result from decreased blood flow through the kidneys. This can be caused by severe dehydration (usually from severe diarrhea or vomiting), heatstroke, or snake bites, and bee stings.
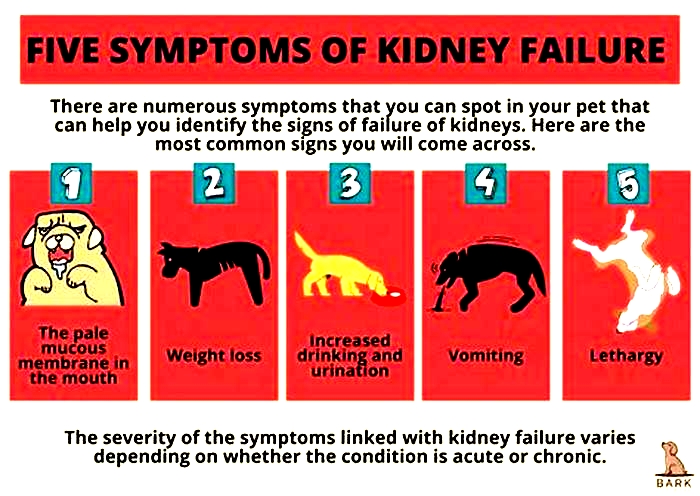
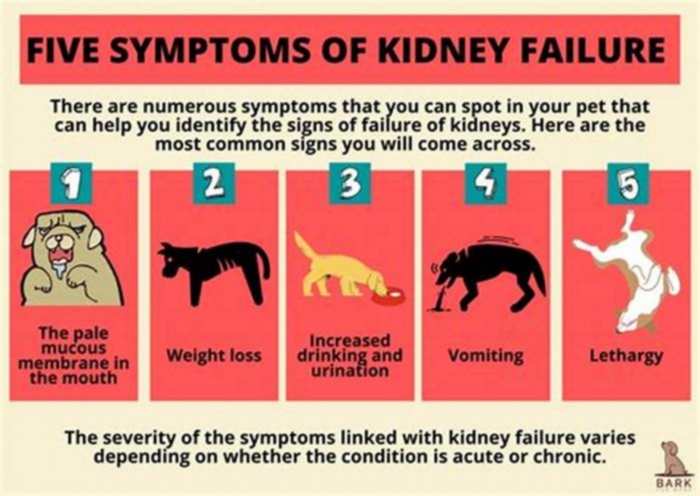
Signs of kidney failure in dogs
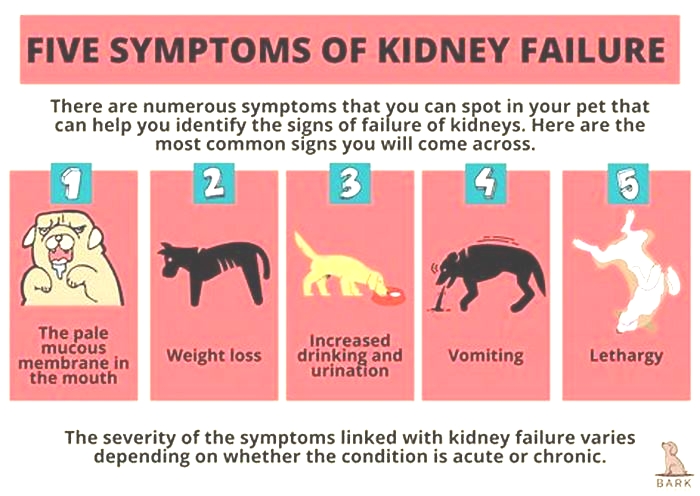
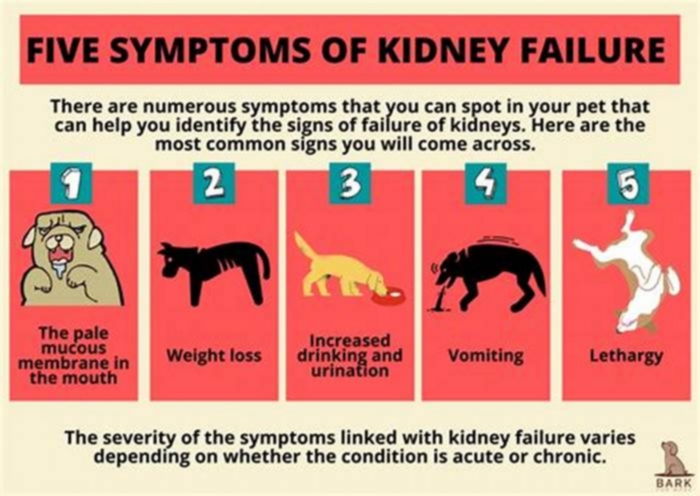
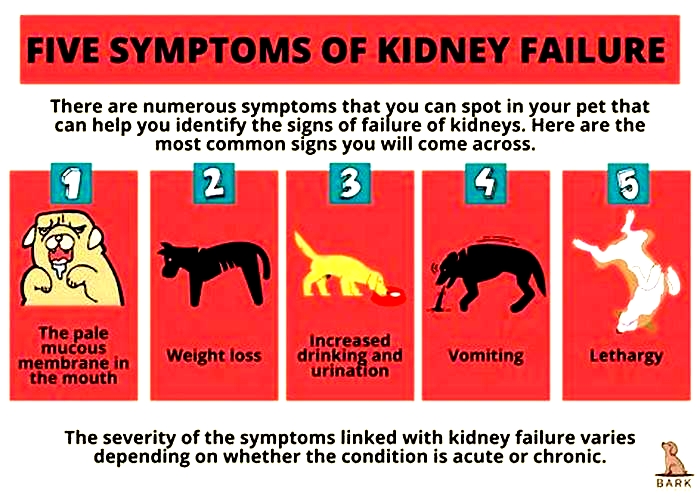
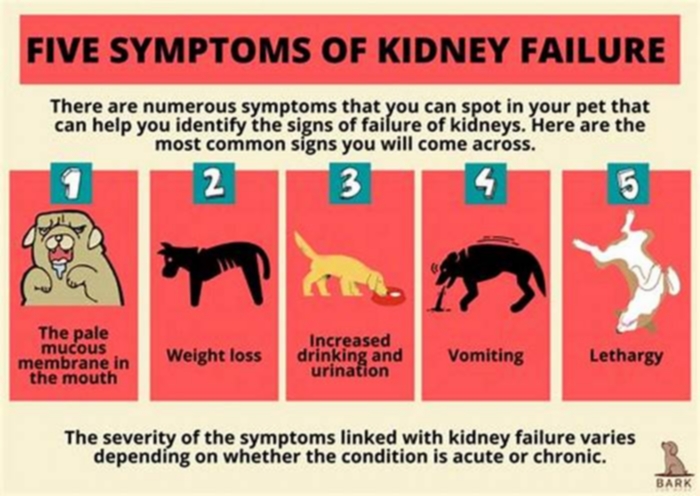
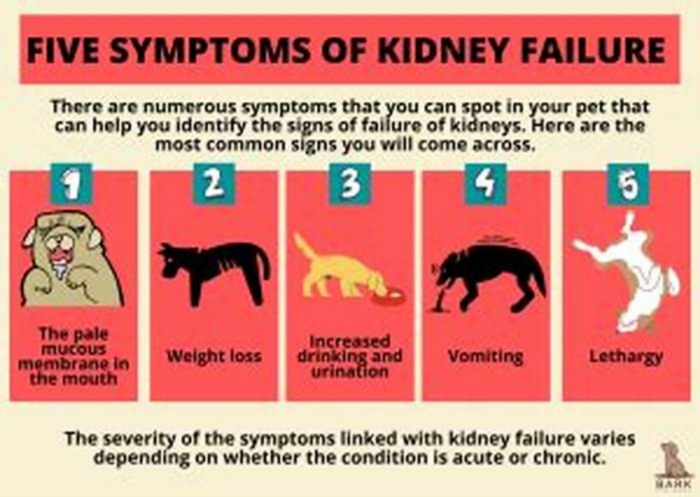
The most common symptoms in dogs with kidney failure include:
- Excessive thirst and urination
- Lethargy
- Decreased appetite
- Weight loss
- Bad breath
- Pale gums
- Vomiting
- Blood in urine
- Ulcers in the mouth
- Uncoordinated movement such as stumbling
- Intestinal seizures
Dogs with chronic renal failure might not show any clinical signs at first, or the signs might be very subtle.
In severe renal failure, the amount of urine might actually decrease, or the dog might stop making urine altogether. As the condition worsens, other symptoms may include blood in the stool, black or tarry stool, or vomiting blood.
Diagnosing kidney failure in dogs
Blood and urine tests are commonly performed to diagnose kidney failure. Other tests, such as ultrasound, X-rays, and special blood tests might be needed in order to assess the severity of the disease and determine the cause for the failure. In some cases, a biopsy of the kidney might be recommended.
How to treat kidney failure in dogs
Treatment for kidney failure in dogs will depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying reason that caused their kidney to fail.
Dogs with acute renal failure can get very ill and might need to be hospitalized. Milder cases can be treated with antibiotics and fluids on an outpatient basis.
In some cases, dialysis might be necessary. Signs that indicate dialysis should be considered include very high potassium levels, lack of improvement in lab results while the pet receives intravenous fluids, and fluid in the lungs. Both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis can be effective but are generally quite expensive.
While damage from acute renal failure is more easily treated, chronic renal failure will cause irreversible damage to your dogs kidneys unless caught early. For that reason, veterinarians generally focus on slowing down the progression of the disease and finding ways to improve the dogs quality of life, usually with medication and diet changes.
Your pups treatment plan might also include:
- Electrolytes to balance out blood levels
- Medications that encourage the production of urine
- Medications to ease gastrointestinal problems
- Medications to reduce vomiting
- Medications for anemia
- Blood pressure management
If kidney disease is left untreated, end-stage renal failure might occur, leading to death. If you suspect your pet has kidney failure, contact your veterinarian or take your dog to an emergency clinic for a diagnosis and treatment.
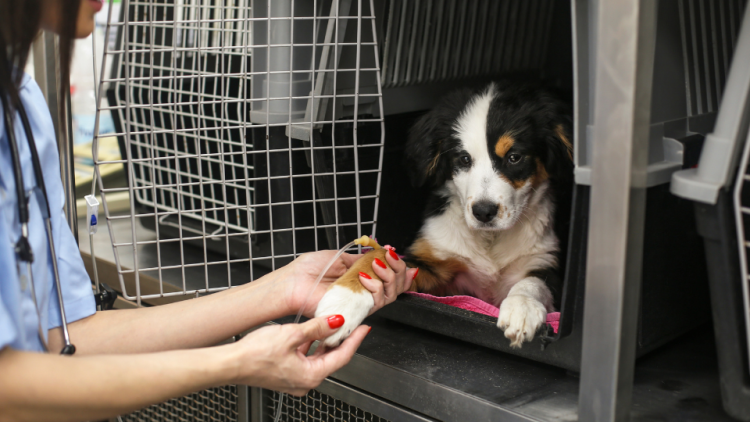

Cost to treat dogs kidney failure
The cost of diagnosis and treatment will also depend on the cause, as well as on how the dog responds. Initial diagnostic tests usually range between $200 and $750, whereas long-term management of chronic kidney failure can cost between $100 and $500 per month, depending on the prescribed medications and how often IV fluid therapy is required.
Pro Tip: Every dog owner should consider pet insurance. Even if you believe you have enough money to cover veterinary costs, pet insurance could still save you thousands of dollars if your dog gets sick or injured.
Whats the prognosis?
Kidney failure is a very serious disease and about 60% of pets suffering from it will either die or be euthanized because of it. In cases when medical treatment has failed, the chance of survival without dialysis is extremely low. About half of the patients that receive dialysis will recover, depending on what caused the failure. Many of them will recover only partially and end up with permanent kidney damage.
However, some pups manage to recover completely and have a good quality of life for years after being diagnosed with the disease.
Talk to your vet about what you should expect after your dog has been diagnosed and treated for kidney failure. The vet might recommend nutritional supplements and/or a therapeutic diet to manage your pups condition.
Preventing kidney failure in dogs
Considering the fact that acute renal failure is usually caused by ingesting toxins or foods like raisins, preventing it is fairly easy. Make sure to get any poisons, medications, and dog-unsafe foods out of your pups reach. You can also get your dog vaccinated for Leptospirosis.
Chronic renal failure is usually age-related and genetically predetermined, so theres not much you can do to prevent it. However, taking your pet for annual wellness checkups and physical exams can increase the chances of catching the disease early and start treatment before it progresses and becomes more serious.