what can be done for a dog in kidney failure
Kidney Failure In Dogs: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options

Kidney disease in dogs is a scary diagnosis for pet parents. After all, we want to spend as much time as possible with our furry family members, and the worries and concerns posed by the possibility of having to say an unexpected goodbye can take their toll. So, what is renal failure in dogs? Lets find out about the causes, the signs and symptoms, the treatment options, and how to know when its time for that final goodbye.
What Causes Kidney Failure In Dogs?
There are lots of causes of kidney failure in dogs. Toxicities from certain foods, anti-freeze, certain medications, and lilies can cause acute renal failure, even in young pets, while in some cases, the kidneys can lose their function slowly with age. Conditions like high blood pressure, cancer, bladder stones, and kidney infections can also contribute to kidney failure.
Which Foods Cause Kidney Failure In Dogs?
Grapes and raisins (and foods that contain them) can lead to kidney failure. This means that the festive period, where cookies, fruit cake, Christmas pudding, panettone, and other raisin-filled treats are everywhere, is a common time to see renal failure in dogs from toxicity.
Unfortunately, the underlying reason why grapes cause kidney damage is unknown, which means that theres no known toxic dose. Some dogs can eat grapes regularly and have no issues, while others can eat just one as a one-off with grave consequences. Therefore, its best to avoid giving your dog grapes altogether and keep them safely out of your dogs reach.
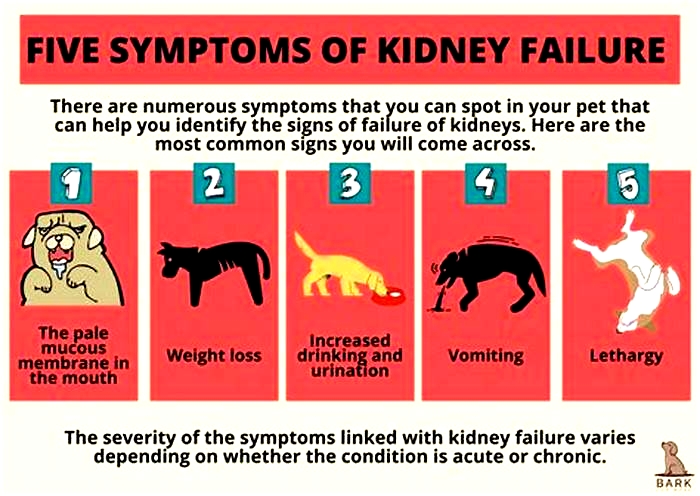
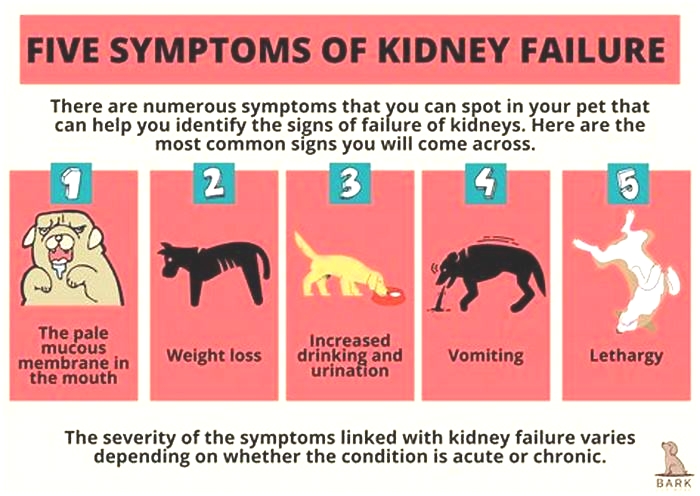
Signs Of Kidney Failure In Dogs
The signs of kidney failure in dogs are variable, depending on the stage of the disease and whether the kidney failure is acute or chronic.
Acute Kidney Failure
If your dog has acute renal failure from a toxin, obstruction, or severe infection, the symptoms are likely to come on very quickly and progress rapidly. You might notice symptoms within a couple of days of the toxicity or sooner in the case of anti-freeze. The first symptoms could be lethargy, pain, vomiting, or increased thirst. This could quickly progress to little or no urination, wobbliness, seizures, coma, or death.
Sadly, in many toxicity situations, once the kidney damage is severe enough to cause symptoms, there is far less chance of treatment being successful. Therefore, if you suspect your dog could have ingested any kind of toxin, call your veterinary clinic immediately so that appropriate measures can be taken to try to prevent any organ damage.
Chronic Kidney Failure
If your dog has chronic kidney disease, their symptoms are likely to be much more subtle and slower to develop. You might initially notice that your dog drinks more than normal or passes large volumes of urine more frequently. You might notice your pup has lost some weight, is vomiting, or hes not so interested in his food anymore. Canines with chronic kidney failure likely also seem to be subdued or lethargic.
As chronic kidney failure progresses, their thirst may become more and more excessive, but despite this, they might become dehydrated, leading to weakness and further lethargy. They may develop ulcers in their mouth, and you might notice an unpleasant smell from their mouth as the toxic waste products build up in their bloodstream. Eventually, theyll stop eating and drinking altogether, become very nauseous, and may seem painful in their abdomen.
What Causes The Symptoms Of Kidney Failure In Dogs?
The role of the kidneys within your dogs body is to control how much water leaves the body, regulate the loss of electrolytes, and remove waste products like urea from the bloodstream. In renal failure, the kidneys are no longer able to produce concentrated urine, so waste products build up in the blood. As more and more of the tiny kidney nephrons are affected, it puts more strain on the remaining parts that still work, which becomes a vicious circle.
The halitosis noted by pet owners who have dogs with chronic kidney failure is due to the build-up of these toxins and is known as a uremic smell. In some dogs, but primarily cats, small blood vessels are damaged by the urea compounds, leading to ulcers in areas like the edge of the tongue.
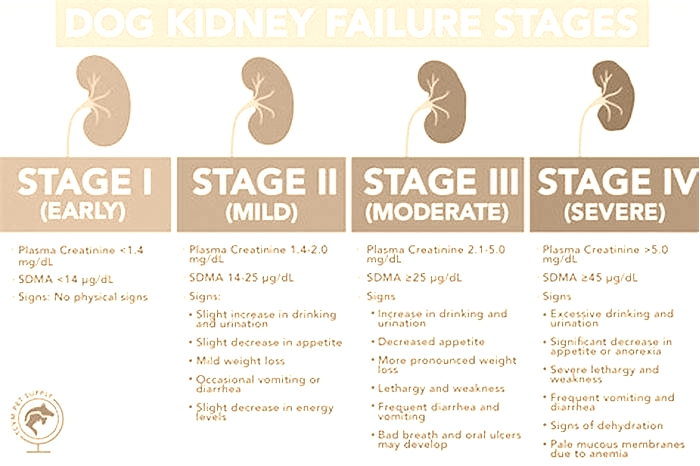
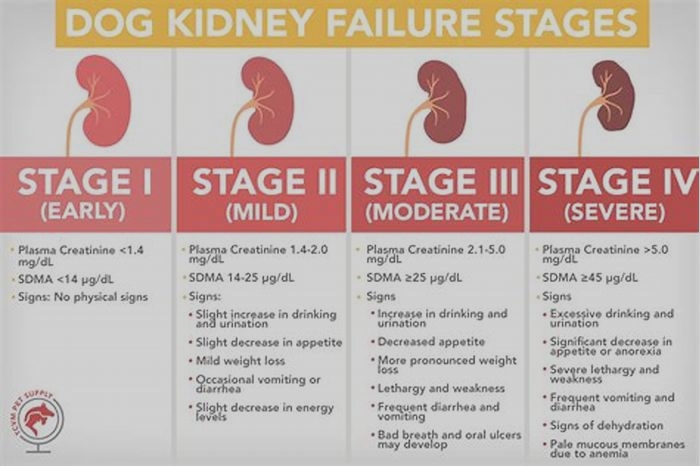
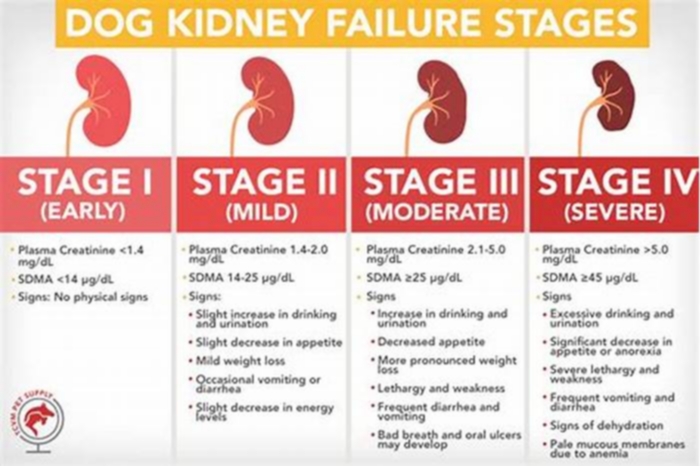
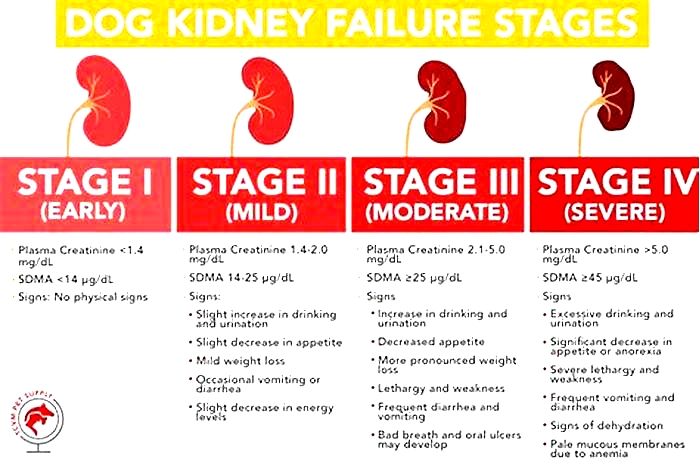
4 Stages Of Kidney Failure In Dogs
When it comes to the symptoms of kidney failure in dogs, stages matter. Kidney failure cases can be grouped into different stages, as formulated by the International Renal Interest Society (IRIS). The symptoms are combined with the urine concentration and blood measurements of urea, creatinine, and SDMA, which are waste products usually excreted by healthy kidneys.
In the early IRIS stages, symptoms are not apparent, whereas later, as the disease progresses, more and more symptoms appear. The IRIS stages of kidney failure in dogs illustrate the amount of kidney damage or the amount of kidney tissue that is still functional. They also aid veterinarians in determining the best treatment and management options.
Dog Kidney Failure Stages Chart
You can see the stages of chronic kidney disease in dogs in the following graphic:
| Stage | Creatinine | SDMA | Urine | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Normal | Normal or slightly raised | May be inadequate concentration, may contain protein | None |
| II | Normal or mildly increased | Mildly raised | Inadequate concentration, may contain protein | None or very mild |
| III | Moderately increased | Moderately raised | Inadequate concentration, may contain protein | Often drinking and urinating more, may be more severe symptoms |
| IV | Markedly increased | Markedly raised | Inadequate concentration, protein likely | Weight loss, vomiting, reduced appetite, drinking and urinating more |
How To Treat Kidney Failure In Dogs
Unfortunately, when a kidney tubule (or nephron) stops working, it cant be fixed. However, treatment and good management can help to slow down the progression of kidney disease and support the remaining functional nephrons. Dogs who are still eating well and arent vomiting may only require a prescription kidney diet.
If their phosphate levels are high, a phosphate binder medication will also help by preventing the absorption of phosphate from their food. If your dog is still in the early stages of chronic kidney disease but isnt eating well or is nauseous, an anti-emetic medication may also be used.
Finally, if your dog has late stage III or stage IV kidney disease, theyll probably need to stay in the hospital for a fluid drip to flush the waste products out of the body and lower the urea and creatinine levels. Unfortunately, this improvement will only be temporary, and over time, the levels will increase once again.
When To Euthanize?
Whenever youre dealing with a chronic health issue in your dog, its really difficult to know when to make the sad decision to euthanize them. After all, theyre likely to have good and bad days, and it might feel like they get a little bit better just when you are about to make the call. The most important thing is to consider your dogs quality of life whether theyre eating, mobile, or showing any signs of pain.
If theyre struggling in more than one of those areas, despite veterinary treatment, its likely to be time to say goodbye. Its also worth looking back over the last two weeks to see how many good and bad days theyve had. If the bad days outweigh the good, euthanasia is the kindest option for your canine companion.

Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about dogs with kidney issues. Dont see yours here? Ask us in our comments.
Does pet insurance cover kidney disease in dogs?
Yes, pet insurance covers kidney disease in dogsas long as no signs or symptoms appear until after policy enrollment and waiting periods have passed.
What happens in the last days of a dog with kidney failure?
In the last days of a dog with kidney failure, theyre likely to stop eating or drinking altogether. They may be weak and wobbly from dehydration, and their other organs may start to fail. If you notice that your dog with kidney failure is deteriorating, you should contact your vet as soon as possible.
Is kidney failure in dogs painful?
Acute kidney failure, due to causes like toxins, infections, or bladder stones, can be very painful and requires emergency assessment by a veterinarian. Chronic renal failure is unlikely to be painful initially, but in the more severe stages of the disease, your dog may feel nauseous, disorientated, or painful.
What is the cost of treating kidney failure in dogs?
The cost of treating kidney failure will vary depending on your location and the type of treatment your dog needs. The most costly would be a fluid drip and hospitalization, but ongoing prescription diets and phosphate binders can also add up in the long term.
How long can a dog live with kidney failure?
The length of time that a dog can live with kidney failure will depend on the stage when the diagnosis was made. If caught early, chronic kidney failure can be managed for several years in some cases. However, if the disease is already advanced or management guidelines arent followed, a dogs quality of life may suffer within a few weeks or months.
What level of creatinine indicates kidney failure in dogs?
A dogs creatinine level should always be evaluated alongside a urine sample. If the urine sample shows poor concentration and the creatinine level is raised, this indicates that the kidneys are not functioning effectively.
Understanding Dogs Health
Kidney disease in dogs is a complex subject, and if the diagnosis is made early, even before your dog shows symptoms, the prognosis is much more favorable. Therefore, it may be a good idea to consider routine blood tests once your dog is older than seven or eight, and you should keep a close eye out for possible symptoms. You might consider an at-home urine test, that can help detect things like kidney stones and urinary tract infections in dogs.
Tagged With:Chronic Renal Failure (CRF) in Dogs
What Is Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs?
Chronic renal failure (CRF), renal insufficiency, and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are all medical terms used to describe the same condition. It occurs when the kidneys are unable to perform their required tasks at the same level of efficiency as before.
Dogs have two kidneys located on either side of their abdomen, that play a vital role in filtering waste from the body. Additionally, the kidneys serve to regulate fluid, mineral, and electrolyte balance; conserve water and protein; and play an important role in maintaining blood pressure and red blood cell production by making a hormone called erythropoietin.
Dogs cannot survive without their kidneys, and unfortunately, kidney transplants are yet to be a viable solution. Dialysis (a treatment for failing kidneys including the removal of waste) is often expensive and is extremely rare in dogs. However, early diagnosis and intervention is key to help maintain your dogs quality of life.
Once diagnosed, CRF is then classified into four different stages based on severity of clinical signs and laboratory values:
Stage I: Clinical signs usually not apparent
Stage II: Some clinical signs noted
Stage III: Many clinical signs noted, and pets often feel sick
Stage IV: Majority of clinical signs noted, pets often present as a crisis
Causes of Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
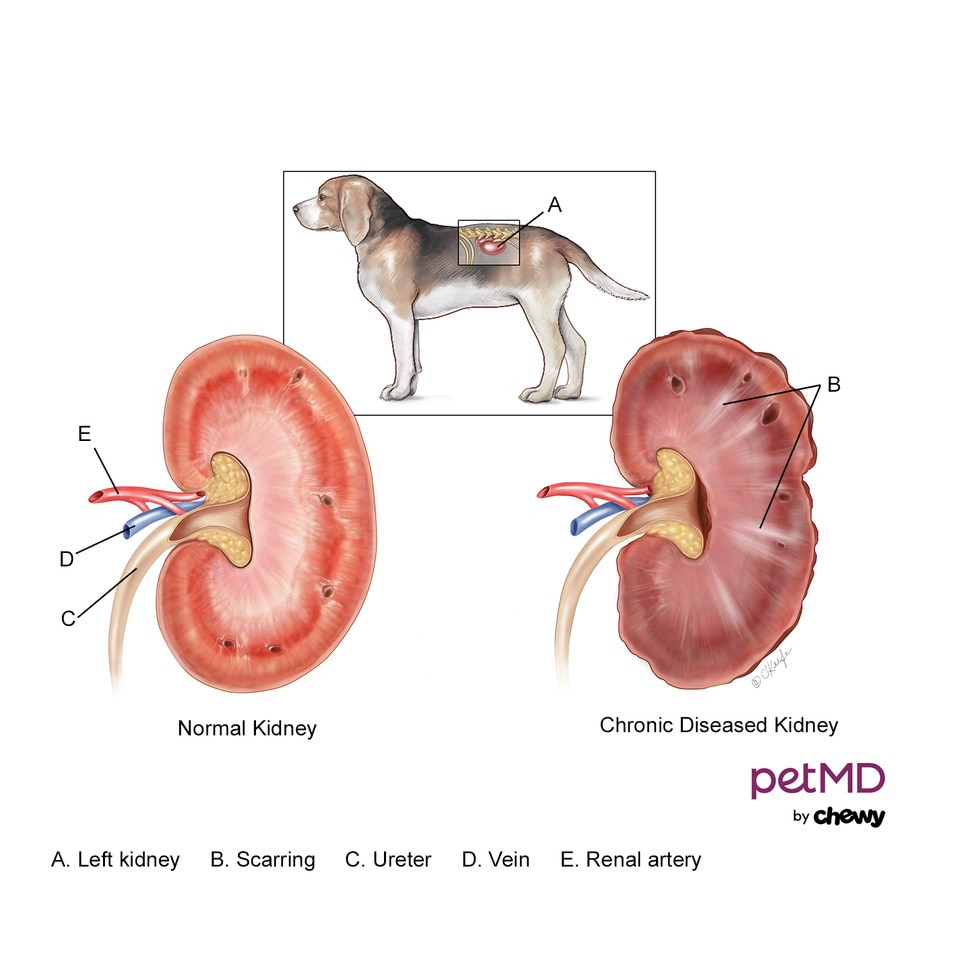
The term chronic in chronic renal failure means that the process has been ongoing, is progressive, and unfortunately, cannot be reversed. For some dogs, the disease could have occurred after a serious kidney injury such as from a severe infection (i.e., leptospirosis, pyelonephritis) or ingestion of a toxic substance such as anti-freeze, grapes, or raisins, and certain antibiotics.
For others, it could be inherited, such as with glomerular disease (a specific type of renal kidney disease) and amyloidosis (a rare organ disease) as seen in breeds like the Bernese Mountain Dog and Shar-pei.
For others, it could be attributed to underlying immune-mediated diseases, stroke-like events, or even from clotting disorders. In cases for newly diagnosed dogs the underlying cause will likely remain unknown.
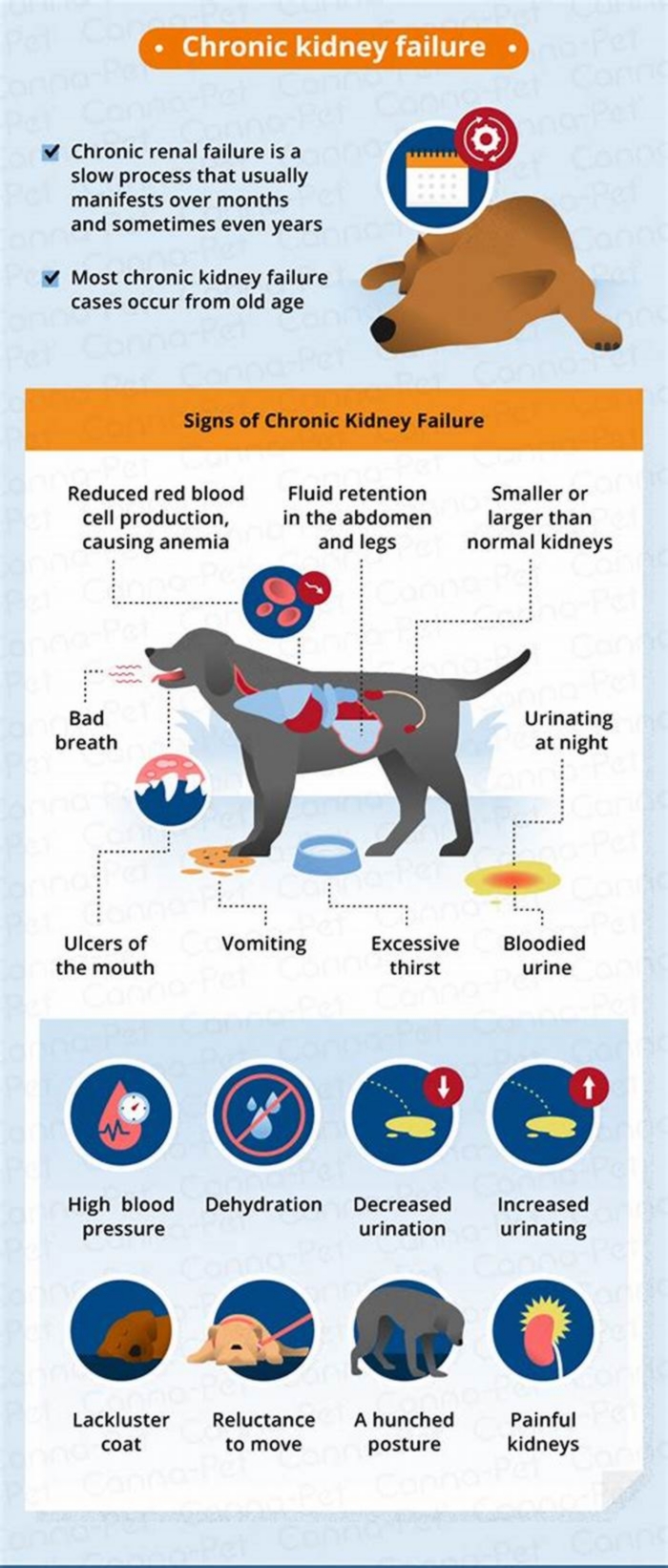
Symptoms of Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
Clinical signs are often related to the severity of the CRF stage, meaning there are additional and more severe signs noted with stages III and IV than there are with stages I and II. Dogs often exhibit symptoms including:
Foul breath
Weight loss
Decreased appetite
Some dogs may show muscle wasting and signs attributed to high blood pressure, such as vision loss and weakness.
How Veterinarians Diagnose Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
CRF is often diagnosed based on routine blood work and a urinalysis looking specifically at kidney markers such as:
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): A by-product of protein metabolism, higher values can often indicate kidney failure
Creatinine (CREA): Measures how well kidneys are filtering waste from blood
Phosphorous: Elevated phosphorus levels typically indicate kidney damage
Electrolytes (Sodium, potassium, chloride)
Calcium
Red blood cell count: A low red blood cell count may indicate kidney failure
Symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA): An additional test to help determine if kidney disease is present; it can be used for early detection of kidney disease
Urine specific gravity: A marker of how diluted or concentrated the urine is. Usually the higher the number, the more concentrated the urine is and the greater ability of the kidney to conserve water.
Your veterinarian will most likely recommend additional diagnostic testing, including:
A urine protein to creatinine (UPC) ratio to quantify how much protein is being lost in the urine
A urine culture, as dogs in CKD are more likely to acquire urinary tract infections
A blood pressure evaluation
Radiographs or abdominal ultrasound to screen for kidney stones or infarcts (areas of dead tissue)
Treatment of Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
Dogs with CRF are generally older and have other ongoing issues, such as arthritis or liver disease, and so the management of CRF can be challenging. However, CRF can be managed, mostly with the aid of medications, diet, and hydration.
Specific management is geared toward each stage of the disease, with each progressive stage recommendations built upon the previous stage recommendations. Any dog in any stage with an increase in either UPC (urine protein to creatinine ratio) or high blood pressure will most likely be treated with medication.
Throughout your dogs life, any disease process or illness that could affect his hydration should be treated promptly with IV fluids. Other drugs will be prescribed based on the dogs diagnosis since renal metabolism will be affected and can lead to overdosages and/or worsening of the kidney disease.
Additionally, for all stages, fresh water should always be available, drinking should be encouraged, and adequate nutrition should be given daily. Dogs diagnosed with CRF are most likely prescribed a kidney friendly diet, which may include feeding your dog a canned diet of wet food that contains additional water.
Recovery and Prevention of Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
As chronic renal failure is not curable and often progressive (although the timeline is variable) in nature, dogs diagnosed early on will benefit from nutritional management and consistent veterinary attention, which may include more frequent check-ups and blood work.
Dogs in stages I and II may often be monitored for further progression of signs, and some may be given a prescription diet specifically geared to help the kidney, by limiting the amount of work they must do.
Many dogs can go on to have a decent quality of life for many months to years. Dogs in stages III and IV often require more medical and dietary assistance. If secondary anemia is present, erythropoietin injections can be given at the direction of your veterinarian.
Dietary supplements, and phosphorus binders (to treat high phosphorus levels) may also be given for low potassium. Anti-nausea and anti-emetic (anti-vomiting) medications can also be prescribed for dogs with a poor appetite, vomiting, or nausea. Fluids given either intravenously or underneath the skin can help dehydration. Because of the severity of signs often seen in dogs with stage III and IV, and the amount of care and effort required to support these dogs, some may be humanely euthanized.
Chronic Renal Failure (CRF) In Dogs FAQs
How long can a dog live with kidney failure without treatment?
Left untreated, dogs in kidney failure will die, usually within a few days to a few weeks. Death is often preceded by loss of appetite, dehydration, weight loss, vomiting, and multi-organ failure.
Can dogs recover from chronic renal failure?
There is no cure for CRF. However, if CRF is caught early and managed correctly, most dogs that experience kidney disease can go on to live a relatively normal life with some changes and long-term management.
Can chronic renal failure in dogs be reversed?
While CRF is not reversible, early treatment can provide your pet with a happier, longer, and fuller life. Regular, semi-annual checkups are key to early diagnosis and treatment of the development of chronic renal disease.
Featured Image: iStock.com/Korneeva_Kristina
WRITTEN BY
Michael Kearley, DVMVeterinarian
Dr. Michael Kearley graduated from the University of Florida College of Veterinary Medicine in 2013. He graduated with a certificate in...