kidney failure in dogs creatinine levels
Creatinine test
Overview
A creatinine test is a measure of how well your kidneys are performing their job of filtering waste from your blood.
Creatinine is a chemical compound left over from energy-producing processes in your muscles. Healthy kidneys filter creatinine out of the blood. Creatinine exits your body as a waste product in urine.
A measurement of creatinine in your blood or urine provides clues to help your doctor determine how well the kidneys are working.
Products & Services
Why it's done
Your doctor or other health care provider may order a creatinine test for the following reasons:
- To make a diagnosis if you have signs or symptoms of kidney disease
- To screen for kidney disease if you have diabetes, high blood pressure or other conditions that increase the risk of kidney disease
- To monitor kidney disease treatment or progression
- To monitor for side effects of drugs that may include kidney damage or altered kidney function
- To monitor the function of a transplanted kidney
How you prepare
A standard blood test is used to measure creatinine levels in your blood (serum creatinine). Your doctor may ask you not to eat (fast) overnight before the test.
For a creatinine urine test, you may need to collect urine over 24 hours in containers provided by the clinic.
For either test, you may need to avoid eating meat for a certain period before the test. If you take a creatine supplement, you'll likely need to stop use.
What you can expect
For a serum creatinine test, a member of your health care team takes a blood sample by inserting a needle into a vein in your arm.
For a urine test, youll need to provide a single sample in the clinic or collect samples at home over 24 hours and return them to the clinic.
Results
Results from creatinine in blood or urine are measured and interpreted in many ways, including the following:
Serum creatinine level
Creatinine usually enters your bloodstream and is filtered from the bloodstream at a generally constant rate. The amount of creatinine in your blood should be relatively stable. An increased level of creatinine may be a sign of poor kidney function.
Serum creatinine is reported as milligrams of creatinine to a deciliter of blood (mg/dL) or micromoles of creatinine to a liter of blood (micromoles/L). The typical range for serum creatinine is:
- For adult men, 0.74 to 1.35 mg/dL (65.4 to 119.3 micromoles/L)
- For adult women, 0.59 to 1.04 mg/dL (52.2 to 91.9 micromoles/L)
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
The measure of serum creatinine may also be used to estimate how quickly the kidneys filter blood (glomerular filtration rate). Because of variability in serum creatinine from one person to another, the GFR may provide a more accurate reading on kidney function.
The formula for calculating GFR takes into account the serum creatinine count and other factors, such as age and sex. A GFR score below 60 suggests kidney disease. The range of scores below 60 may be used to monitor treatment and disease progression.
Creatinine clearance
Creatinine clearance is a measure of how well the kidneys filter creatinine out of the bloodstream for excretion in urine.
Creatinine clearance is usually determined from a measurement of creatinine in a 24-hour urine sample and from a serum sample taken during the same time period. However, shorter time periods for urine samples may be used. Accurate timing and collection of the urine sample is important.
Creatinine clearance is reported as milliliters of creatinine per minute per body surface area (mL/min/BSA). The typical range for men, 19 to 75 years old, is 77 to 160 mL/min/BSA.
The typical range, by age, for creatinine clearance in women is as follows:
- 18 to 29 years: 78 to 161 mL/min/BSA
- 30 to 39 years: 72 to 154 mL/min/BSA
- 40 to 49 years: 67 to 146 mL/min/BSA
- 50 to 59 years: 62 to 139 mL/min/BSA
- 60 to 72 years: 56- to 131 mL/min/BSA
Standard measures have not been determined for older adults.
Results lower than the typical range for your age group may be a sign of poor kidney function or conditions that affect blood flow to your kidneys.
Albumin/creatinine ratio
Another interpretation of urine creatinine count is called the albumin/creatinine ratio. Albumin is a protein in blood. Healthy kidneys generally don't filter it out of the blood, so there should be little to no albumin found in the urine.
Albumin/creatinine ratio describes how much albumin is in a urine sample relative to how much creatinine there is. The results are reported as the number of milligrams (mg) of albumin for every gram (g) of creatinine. Results indicating a healthy kidney are:
- For adult men, less than 17 mg/g
- For adult women, less than 25 mg/g
A higher than typical result may be a sign of kidney disease. In particular, the result may indicate a complication of diabetes called diabetic nephropathy, or diabetic kidney disease.
Your doctor or other health care provider will discuss the results of a creatinine test with you and help you understand what the information means for a diagnosis or treatment plan.
Feb. 09, 2023
Kidney Disease in Dogs: Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment
Your dogs kidneys are essential organs that filter waste products from the bloodstream. When the kidneys are weakened, either by acute or chronic kidney disease, your dogs health could suffer. Because kidney disease progresses over time, its important to learn the common symptoms so tha you can recognize them. If you catch kidney disease in dogs early on, treatment can slow down the progression and allow your dog to live longer.
What Is Kidney Disease in Dogs?
Kidney disease in dogs is sometimes called renal or kidney insufficiency because it occurs when a dogs kidneys stop doing their job as efficiently as they should. The main job of the kidneys is to help clear and excrete waste products from the blood and convert them to urine, says Dr. Jerry Klein, Chief Veterinary Officer for the AKC. If the kidneys are not working properly, these waste products can build up in the blood, causing detrimental effects.
Dogs can get either acute kidney disease, which develops suddenly, or chronic kidney disease (CKD), which develops slowly and worsens over an extended period. Both involve loss of kidney function, but they result from different circumstances. Acute kidney disease is a sudden attack or injury to the kidney, whereas chronic kidney disease is a slow, degenerative loss of kidney function, Dr. Klein explains.
What Causes Kidney Disease in Dogs?
Dr. Klein warns that kidney disease could be caused by a lot of things, including infection (such as with the bacteria that causes leptospirosis), trauma, genetics, drugs, toxins, cancer, mechanical obstructions (like kidney stones), and degenerative diseases (where the job and form of the affected body part get worse over time). Anything that decreases blood flow to the kidneys, such as dehydration or heatstroke, can cause the kidneys to fail.
Acute kidney disease in dogs can be caused by exposure to hazardous materials, including toxic plants such as lilies, certain drugs, harmful foods such as grapes or raisins, or antifreeze. Puppy-proofing your home and yard can keep your dog away from potentially harmful items or foods that could be toxic.
Chronic kidney disease in dogs is also associated with growing older. Because kidney tissue cant regenerate once its damaged, the kidneys can wear out over time. As small-breed dogs often live longer than large-breed dogs, they tend to show early signs of kidney disease at an older age10 years old or more, compared to as young as 7 for the large breeds.
What Are the Symptoms of Kidney Disease in Dogs?
The earliest signs of kidney disease in dogs are increased urination and therefore increased thirst. Other symptoms dont usually become apparent until about two-thirds of the kidney tissue is destroyed. So, in the case of CKD, the damage may have begun months or even years before the owner notices. Because of this, its common for the signs of kidney disease in dogs to seem like they came out of the blue when in fact, the kidneys have been struggling for a long time.
Other signs of chronic kidney disease in dogs to watch for include:
Dr. Klein says there are some rarer symptoms of kidney disease in dogs to be aware of, as well. On occasion, there can be abdominal painurinary obstructions or stonesand in certain instances, one can see ulcers in the oral or gastric cavity. In extreme cases, little or no urine is produced at all.
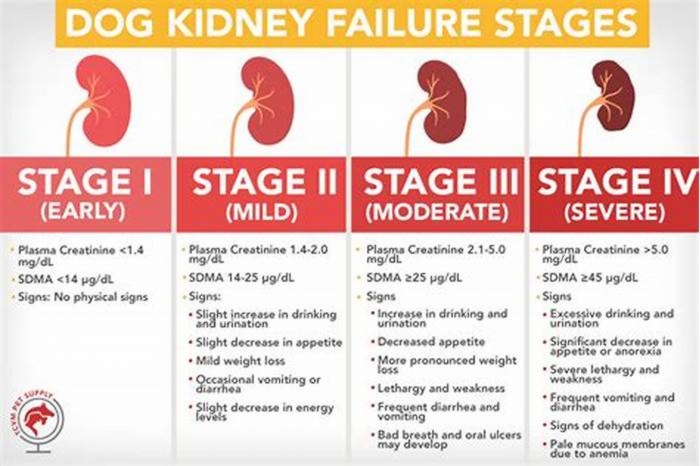
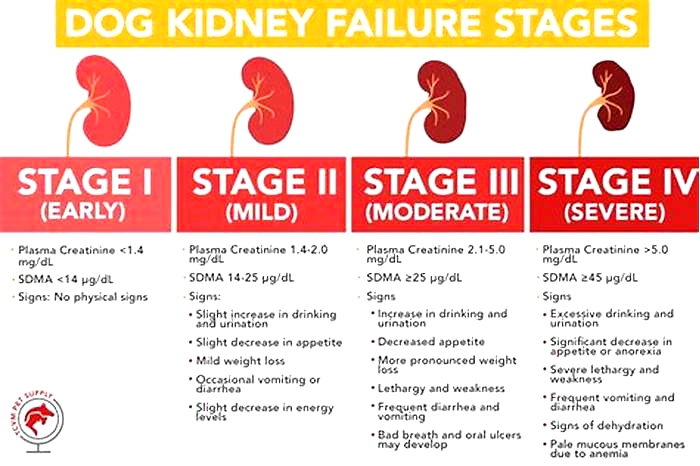
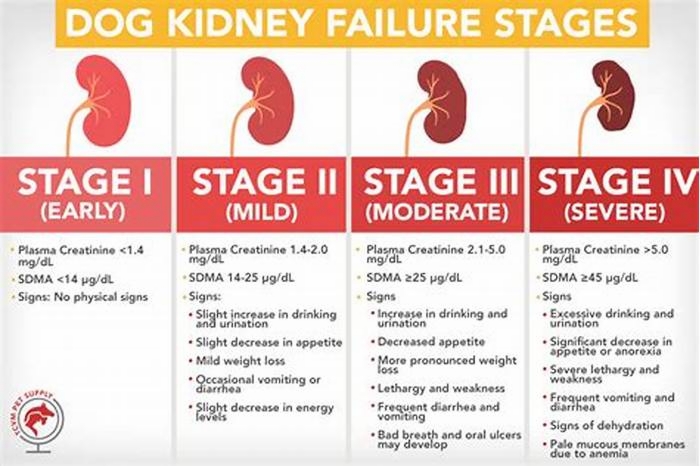
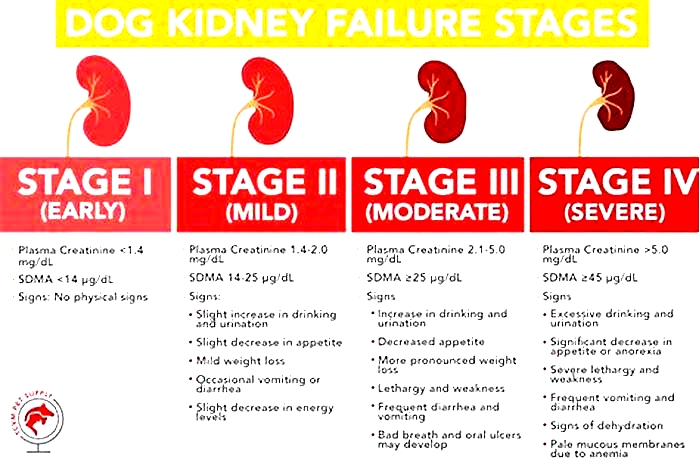
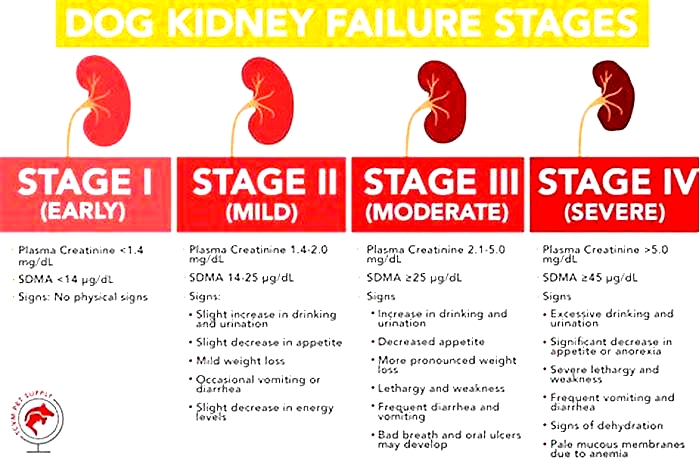
What Are the Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease in Dogs?
Kidney disease in dogs is measured in stages. Many veterinarians use the IRIS scale, which has four stages. Blood work measurements like creatinine and SDMA (biomarkers for kidney function) allow your vet to assign your dog to a particular stage which will determine the exact treatment.
Dr. Klein explains, The stages determine how well the kidneys can filter waste and extra fluid from the blood. As the stages go up, the kidney function worsens. In the early stages of CKD, the kidneys are still able to filter out waste from the blood. In the latter stages, the kidneys must work harder to filter the blood and in late stages may stop working altogether.
How Is Kidney Disease in Dogs Treated?
Dialysis (a medical procedure that removes waste products and extra fluid from the blood) is far more common in humans than in dogs, although peritoneal (kidney) dialysis can be performed in some cases. On rare occasions, surgical kidney transplant is possible in dogs.
But Dr. Klein specifies that depending on the type and stage of kidney disease, the main treatments for CKD are diet changes and administration of fluids, either directly into the veins (intravenous) or under the skin (subcutaneous). The balancing and correction of electrolytes are extremely important in the management of kidney patients, he explains.
Proper nutrition is needed, and there are many available diets formulated for cats and dogs with kidney issues, some by prescription only. Your veterinarian can help guide you to the most appropriate diet for your pet.
Because kidney disease, particularly in the late stages, can cause a dog to lose their appetite, it can be difficult to encourage your dog to eat enough. Dr. Klein advises, There are medications used as appetite stimulators available, such as the prescription drug mirtazapine. Capromorelin has recently been FDA-approved for dogs to address appetite in chronic kidney disease.
When Do You Need to Call Your Vet?
The prognosis and expected life span for a dog with kidney disease depend on the type of disease, the speed of progression, and underlying conditions present in the dog. However, the more serious the disease, the poorer the outcome. Thats why its so crucial to catch the illness early on.
According to Dr. Klein, In chronic kidney disease, there are methods, such as diets and medications, that can be used to lessen the burden of work the kidneys need to do and may help slow down the progression from one stage to the next. In acute kidney disease, there is less time and fewer choices available to prevent further damage to the kidneys and to try to jump-start the kidneys to get them to function normally.
Regular veterinary exams, including bloodwork, are an excellent way to spot kidney problems before the outward symptoms become apparent. And if you notice any of the above signs, dont hesitate to get your dog to the vet for further testing. It can make a huge difference in preserving kidney function and your dogs well-being for as long as possible.
Kidney Failure in Dogs
What Is Kidney Failure in Dogs?
The primary job of the kidneys is to filter the blood by removing waste products and controlling the amount of fluid and nutrients kept in the body and how much is passed in urine.
With any type of kidney failure, this filtering isnt working well, so waste products are not properly removed from the bloodstream and too much fluid is passed in urine along with proteins and electrolytes. As waste products build up in the blood and tissues, dogs can get ulcerations (tears) in the lining of their digestive tract as well.
Kidney failure may also be referred to by terms listed below. The word renal refers to all things related to kidneys, and is often used interchangeably. Failure, insufficiency, and disease are commonly used to describe similar issues with the kidneys.
Kidney disease is often divided into categories based on how long it has been affecting the dog. Acute renal failure occurs in a very short time frame, and is often caused by eating or drinking a toxin or getting a severe infection that harms the kidneys. Chronic kidney disease refers to a process with a more gradual onset or one that has been happening for a longer period of time.
Changes that can occur with an aging pet are often caused by chronic kidney disease, but if a dogs kidneys were damaged by eating a toxic item several months ago and he now has renal failure because of this, it is also known as chronic kidney disease.
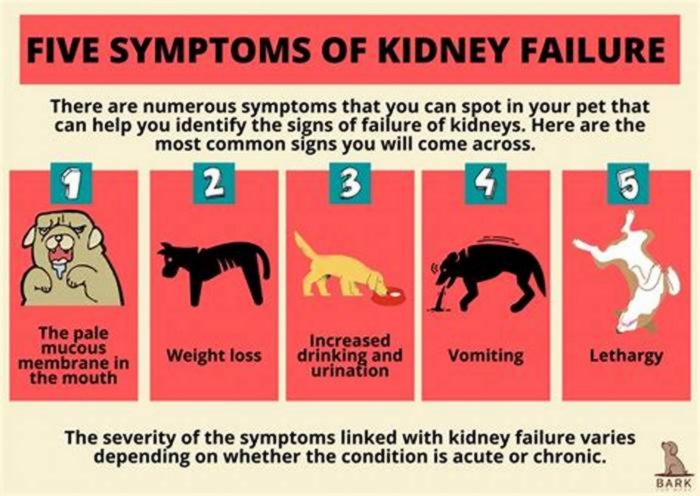
Symptoms of Kidney Failure in Dogs
Drinking more water (polydipsia)
More frequent urination (polyuria)
Urinary accidents in house-trained pets
Lack of energy
Refusing to eat
Vomiting
Drooling
Changes in defecation (either diarrhea or constipation)
Weight loss
Mouth sores
Bad breath
Weakness
Causes of Kidney Failure in Dogs
Kidney failure can occur because of an acute event, such as a toxin ingestion or infection that harms the kidneys; degenerative (worsening) changes over time; or an underlying medical condition that damages renal tissues, which can occur due to genetic predispositions in some dog breeds.
Specific causes include:
Ingested toxins
Metabolic diseases
Kidney infections
Autoimmune disease
Cancers
Breeds that are prone to inherited renal failure include:
How Veterinarians Diagnose Kidney Failure in Dogs
Your veterinarian will want to run several tests, in addition to a physical exam, to diagnose kidney failure, such as:
Complete blood count
Chemistry panel
Urinalysis with culture
Abdominal ultrasound
Treatment of Kidney Failure in Dogs
Treatment of kidney failure is based on the severity of the disease and whether it is acute or chronic.
Acute kidney disease is treated with hospitalization and IV fluid therapy to support the kidneys and help them remove wastes. Depending on the cause of the disease, decontamination medications, toxin-binding medications, antibiotics, or medications to support the gastrointestinal tract may be given. In extreme cases, renal dialysis can help the kidneys. This last procedure is rare, only available at some university or veterinary specialty hospitals.
Chronic kidney disease requires careful management of dogs at home. They need to have access to water at all times and be encouraged to drink water. Many dogs have improvements with a prescription kidney diet. Some dogs need to be on medications to control high blood pressure or to protect their stomach. Pets with chronic kidney disease need to see their veterinarian often so that their renal values can be checked. Some dogs with kidney disease need to receive injectable fluids at home or may even need to be hospitalized at times to help their fluid needs.
Recovery and Management of Kidney Failure in Dogs
With acute kidney failure, prognosis is variable depending upon the cause of the disease, how severe the disease is, how damaged the kidneys are, the speed and aggressiveness of treatment, and the dogs response.
For chronic renal failure, long-term prognosis is not good. Most dogs die or are euthanized within a year because of poor quality of life.
The families of dogs with kidney disease should expect to watch them closely and will need to see their veterinarian often, especially as their pets kidney function gets worse. These dogs will be easily dehydrated, as their kidneys are not able to keep water in their bodies. Any infection, vomiting, diarrhea, or changes in appetite or activity could severely dehydrate the pet and worsen the disease.
Kidney Failure in Dogs FAQs
How does kidney failure differ from kidney disease?
Kidney disease is a broader term that includes any problem with the kidneys. Kidney failure is a specific term that means the kidneys cant keep up with filtering waste products and managing fluid levels.
Is kidney failure fatal in dogs?
Depending on the severity and progression of the disease, kidney failure can be fatal.
WRITTEN BY
Laura Russell, DVM, MBA, DABVPVeterinarian
Dr. Russell is a 2003 graduate of the University of Missouri. She is board certified in Canine and Feline Practice, certified in canine...