is kidney failure in a dog painful
What Are the Symptoms of a Dog Dying From Kidney Failure?

If your dog has been diagnosed with this renal disease or you're worried they're showing signs associated with end-stage kidney failure, a lot is probably going through your mind right now. At the forefront might be which stage of kidney disease does your dog fall under, and how can you make them as comfortable as possible? It's advisable to educate yourself about what to expect as your pet's illness progresses. That way, you can give them the best quality of life all the way through their final days.
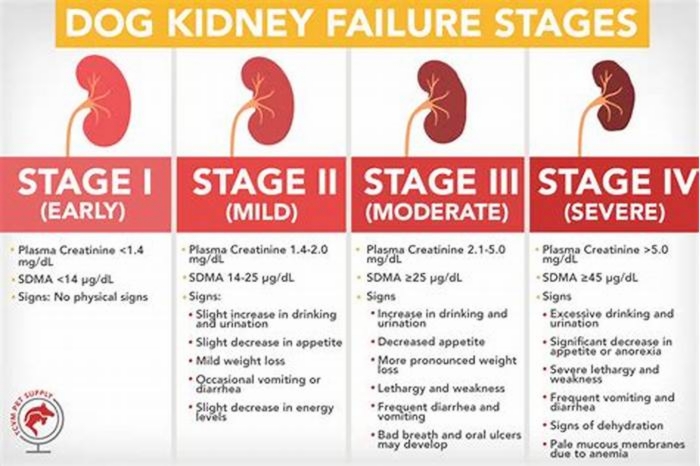
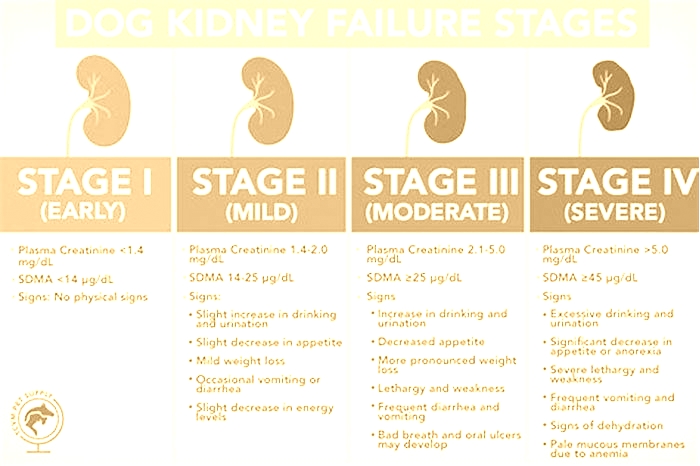
Dog Kidney Failure Stages
Dogs with kidney failure go through a series of four stages, from diagnosis through the eventual death of the animal. These stages do not necessarily occur within rapid succession. A dog can go through them over the course of a few months or even years. Veterinarians determine the stage your dog is in by testing the urine to look for signs of the deterioration of the kidney's functions and the blood for symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) levels.
The Four Stages of Kidney Failure Chart
The canine kidney failure stages are determined by the levels of creatinine and SDMA, as well as the urine-to-protein (UPC) ratio and the animal's systolic blood pressure.
| Dog Kidney Failure Stage | Creatinine (in mg/dL) | SDMA (in g/dL) |
| Stage 1 | less than 1.4 | less than 18 |
| Stage 2 | 1.4 to 2.0 | 18 to 35 |
| Stage 3 | 2.1 to 5.0 | 36 to 54 |
| Stage 4 | greater than 5.0 | greater than 54 |
Other clinical indications that a dog is in the stages of kidney failure are:
- UPC Ratio:
- Nonproteinuric: less than 0.2
- Borderline proteinuric: 0.2 to 0.5
- Proteinuric: greater than 0.5
- Systolic blood pressure (in mmHg):
- Normotensive: less than 150
- Borderline hypertensive: 150 to 159
- Hypertensive: 160 to 179
- Severely hypertensive: greater than 180
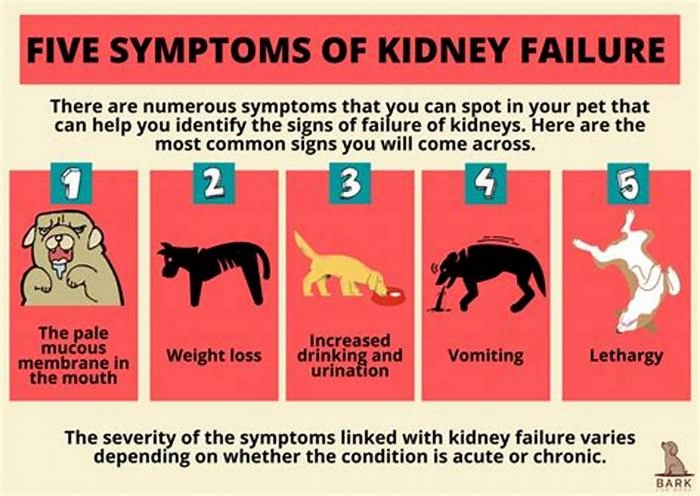
Symptoms of End-Stage Kidney Failure in Dogs
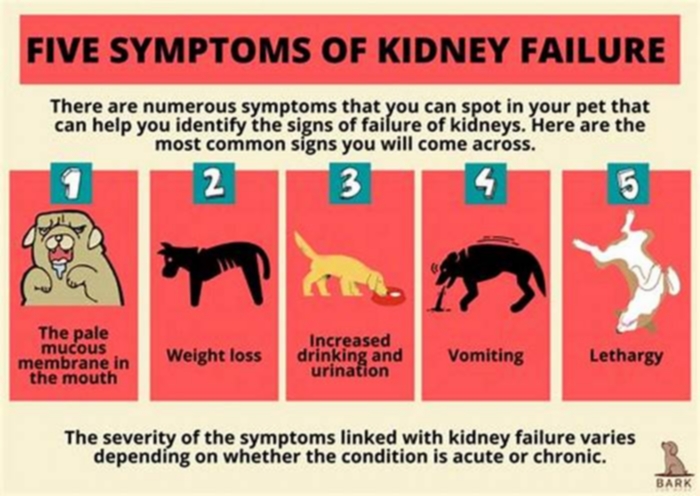
The most common signs a dog is dying from kidney failure include:
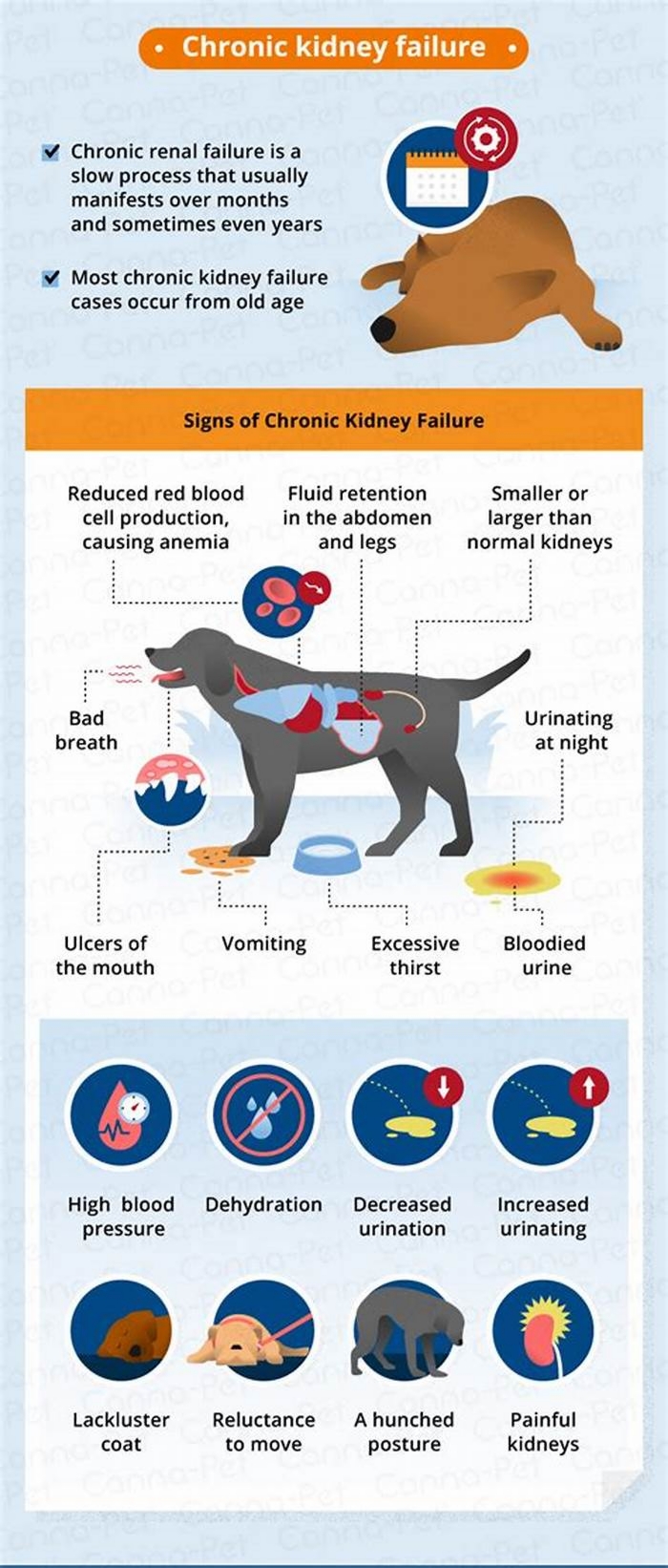
- Uremia: The buildup of waste products in the body produces a distinctive ammonia smell that is especially apparent on the breath.
- Pale, dry gums: The gums are duller and dry to the touch.
- Mouth ulcers: Uremia causes raw mouth ulcers that are painful.
- Bloodshot eyes: The whites of the eyes are bloodshot.
- Increased thirst: An affected dog drinks water excessively.
- Increased urination: The dog will urine large volumes of dilute urine.
- Dehydration: Despite more fluid intake, the dog is dehydrated.
- Decreased appetite: The dog loses interest in food.
- Weight loss: The dog steadily loses weight.
- Gradual loss of fat and muscle mass: The weight loss affects both fat and muscle mass and can cause emaciation.
- Dull coat that sheds excessively: The lackluster coat constantly sheds and looks unkempt.
- Lethargy: The dog has little energy or interest in moving around.
- Fatigue: The dog sleeps most of the day and night with only brief periods of wakefulness.
- Vomiting: The dog vomits frequently and cannot keep food down.
- Anemia: The dog may develop anemia.
- High blood pressure: The dog has elevated blood pressure.
- Incontinence: A dog cannot control their urination.
- Difficulty breathing: The dog has problems breathing normally.
- Slowing heart rate: A faster heart rate is generally present with kidney failure, but the heart rate begins to slow down during the end stage of the disease.
- Depression: The dog seems sad and does not respond to any of their favorite things.
- Low temperature: Dogs in their last days of kidney failure can experience hypothermia or a low body temperature.
- Lack of interest in surroundings: The dog is unaware of or disinterested in their surroundings.
- Disorientation: The dog acts confused at times.
- Loss of balance and coordination: The dog appears clumsy and unsteady on their feet.
- Trembling or shaking: The dog has tremors or episodes of shaking.
- Seizures: The dog suffers periodic seizures, one of the major signs of end-stage kidney failure.
Keeping Your Pet Comfortable
Watching your pet go through this can be very difficult. However, there are things you can do to help keep your dog comfortable during the final stages of kidney disease.
- Spend as much time as possible with your dog. Even being in the same room will be soothing to them.
- Make sure your dog's resting area is quiet, warm, and cozy. Provide them with their favorite blanket and toy.
- Protect your pet from other pets or people who may be too rough with them. Supervise interactions with children and teach them to be gentle with the dog.
- Pet your dog and talk to them frequently.
- Change your dog's bedding often and keep them clean and dry. Brush their fur for dry cleaning. Clean their fur with a sponge bath solution of hypoallergenic pet shampoo.
- Feed your pet a low-protein dog food appropriate for a kidney failure diet.
- If your dog refuses to eat or has trouble eating, ask the veterinarian about other feeding options such as an esophagostomy tube to keep them nourished.
- Monitor your dog's temperature and keep them warm with plenty of cozy blankets.

Last Days of a Dog Dying From Kidney Failure
While a dog owner may fear that entering the final stage of kidney failure means their dog's passing away is imminent, it is difficult to predict how long the does has left. In general, you can expect your dog to pass away within three months of moving into stage 4, though some dogs may thrive for up to a year.
It depends on the associated symptoms and other conditions that may arise due to the dog's poor health. Your dog's age is another factor. There's a lot to keep in mind, a lot to hope for, and the reality that you're facing the end of your dog's life.
Fast Fact
Controlling your dog's diet can help during their struggle with renal failure. Carefully discuss nutrition with your dog's veterinarian.
When to Consider Euthanization
When a dog enters end-stage renal failure, your veterinarian may recommend an end-of-life home treatment plan or a hospice program to make your pet's last days comfortable and maintain your pet's quality of life. For end-stage kidney failure, a treatment plan may include dialysis, a stomach tube, intravenous therapy, pain medication, and methods to care for an incontinent pet.
Depending on their symptoms, your dog may not necessarily be in severe pain, but they will be uncomfortable at the least from other symptoms, including frequent vomiting and diarrhea, lethargy and depression, and constant dehydration. Your veterinarian may recommend euthanasia if a dog is suffering, unresponsive to pain management, or too weak to handle necessary life-sustaining treatment.
Dealing With the Loss
It's hard to come to terms with the fact that a pet is dying. Find comfort in the fact that your dog appreciates your loving care in their final days. They know you love them and take comfort in your presence and all that you do to make their life easier.
2024 LoveToKnow Media. All rights reserved.
Chronic Renal Failure (CRF) in Dogs
What Is Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs?
Chronic renal failure (CRF), renal insufficiency, and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are all medical terms used to describe the same condition. It occurs when the kidneys are unable to perform their required tasks at the same level of efficiency as before.
Dogs have two kidneys located on either side of their abdomen, that play a vital role in filtering waste from the body. Additionally, the kidneys serve to regulate fluid, mineral, and electrolyte balance; conserve water and protein; and play an important role in maintaining blood pressure and red blood cell production by making a hormone called erythropoietin.
Dogs cannot survive without their kidneys, and unfortunately, kidney transplants are yet to be a viable solution. Dialysis (a treatment for failing kidneys including the removal of waste) is often expensive and is extremely rare in dogs. However, early diagnosis and intervention is key to help maintain your dogs quality of life.
Once diagnosed, CRF is then classified into four different stages based on severity of clinical signs and laboratory values:
Stage I: Clinical signs usually not apparent
Stage II: Some clinical signs noted
Stage III: Many clinical signs noted, and pets often feel sick
Stage IV: Majority of clinical signs noted, pets often present as a crisis
Causes of Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
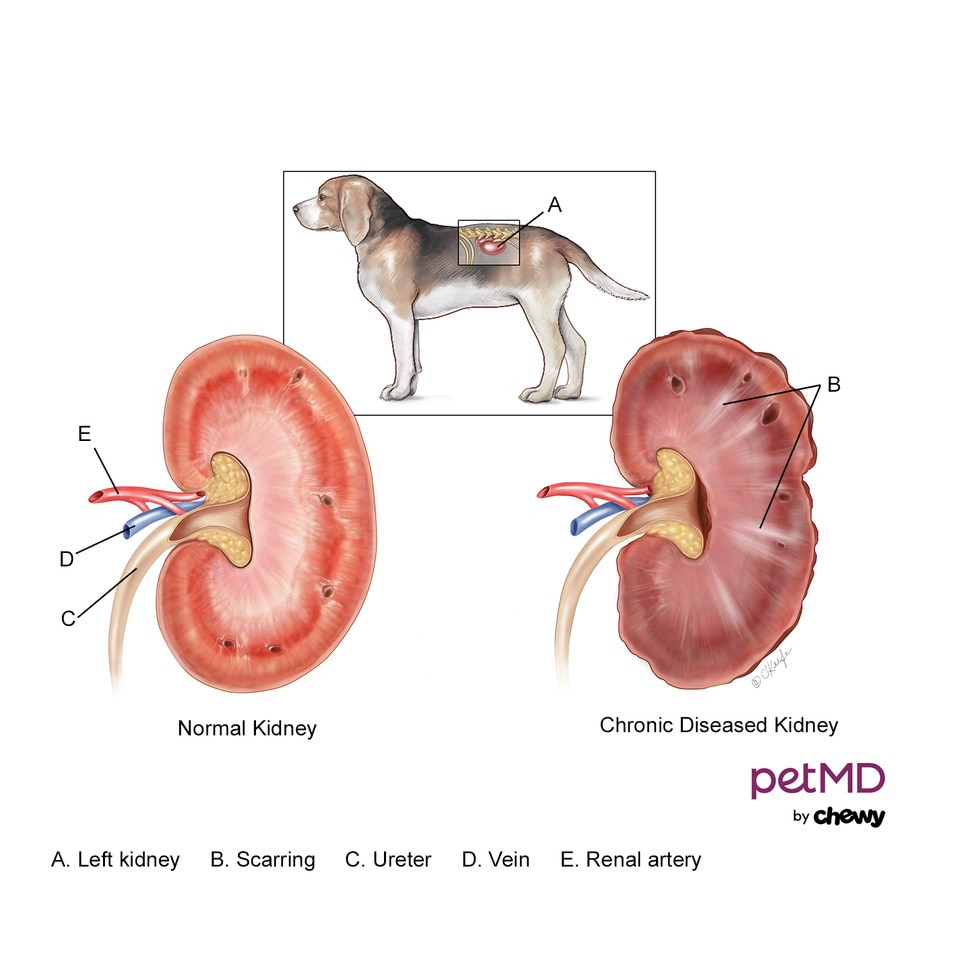
The term chronic in chronic renal failure means that the process has been ongoing, is progressive, and unfortunately, cannot be reversed. For some dogs, the disease could have occurred after a serious kidney injury such as from a severe infection (i.e., leptospirosis, pyelonephritis) or ingestion of a toxic substance such as anti-freeze, grapes, or raisins, and certain antibiotics.
For others, it could be inherited, such as with glomerular disease (a specific type of renal kidney disease) and amyloidosis (a rare organ disease) as seen in breeds like the Bernese Mountain Dog and Shar-pei.
For others, it could be attributed to underlying immune-mediated diseases, stroke-like events, or even from clotting disorders. In cases for newly diagnosed dogs the underlying cause will likely remain unknown.
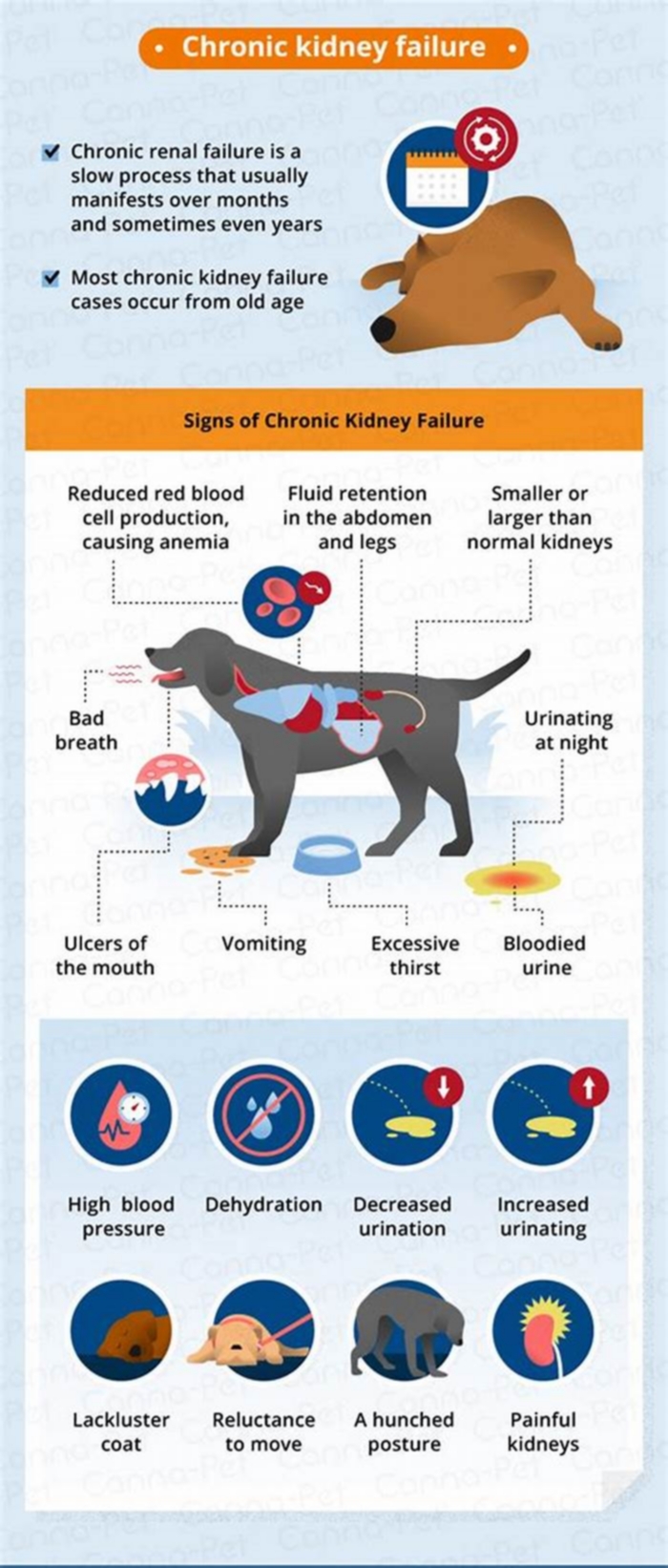
Symptoms of Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
Clinical signs are often related to the severity of the CRF stage, meaning there are additional and more severe signs noted with stages III and IV than there are with stages I and II. Dogs often exhibit symptoms including:
Foul breath
Weight loss
Decreased appetite
Some dogs may show muscle wasting and signs attributed to high blood pressure, such as vision loss and weakness.
How Veterinarians Diagnose Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
CRF is often diagnosed based on routine blood work and a urinalysis looking specifically at kidney markers such as:
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): A by-product of protein metabolism, higher values can often indicate kidney failure
Creatinine (CREA): Measures how well kidneys are filtering waste from blood
Phosphorous: Elevated phosphorus levels typically indicate kidney damage
Electrolytes (Sodium, potassium, chloride)
Calcium
Red blood cell count: A low red blood cell count may indicate kidney failure
Symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA): An additional test to help determine if kidney disease is present; it can be used for early detection of kidney disease
Urine specific gravity: A marker of how diluted or concentrated the urine is. Usually the higher the number, the more concentrated the urine is and the greater ability of the kidney to conserve water.
Your veterinarian will most likely recommend additional diagnostic testing, including:
A urine protein to creatinine (UPC) ratio to quantify how much protein is being lost in the urine
A urine culture, as dogs in CKD are more likely to acquire urinary tract infections
A blood pressure evaluation
Radiographs or abdominal ultrasound to screen for kidney stones or infarcts (areas of dead tissue)
Treatment of Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
Dogs with CRF are generally older and have other ongoing issues, such as arthritis or liver disease, and so the management of CRF can be challenging. However, CRF can be managed, mostly with the aid of medications, diet, and hydration.
Specific management is geared toward each stage of the disease, with each progressive stage recommendations built upon the previous stage recommendations. Any dog in any stage with an increase in either UPC (urine protein to creatinine ratio) or high blood pressure will most likely be treated with medication.
Throughout your dogs life, any disease process or illness that could affect his hydration should be treated promptly with IV fluids. Other drugs will be prescribed based on the dogs diagnosis since renal metabolism will be affected and can lead to overdosages and/or worsening of the kidney disease.
Additionally, for all stages, fresh water should always be available, drinking should be encouraged, and adequate nutrition should be given daily. Dogs diagnosed with CRF are most likely prescribed a kidney friendly diet, which may include feeding your dog a canned diet of wet food that contains additional water.
Recovery and Prevention of Chronic Renal Failure in Dogs
As chronic renal failure is not curable and often progressive (although the timeline is variable) in nature, dogs diagnosed early on will benefit from nutritional management and consistent veterinary attention, which may include more frequent check-ups and blood work.
Dogs in stages I and II may often be monitored for further progression of signs, and some may be given a prescription diet specifically geared to help the kidney, by limiting the amount of work they must do.
Many dogs can go on to have a decent quality of life for many months to years. Dogs in stages III and IV often require more medical and dietary assistance. If secondary anemia is present, erythropoietin injections can be given at the direction of your veterinarian.
Dietary supplements, and phosphorus binders (to treat high phosphorus levels) may also be given for low potassium. Anti-nausea and anti-emetic (anti-vomiting) medications can also be prescribed for dogs with a poor appetite, vomiting, or nausea. Fluids given either intravenously or underneath the skin can help dehydration. Because of the severity of signs often seen in dogs with stage III and IV, and the amount of care and effort required to support these dogs, some may be humanely euthanized.
Chronic Renal Failure (CRF) In Dogs FAQs
How long can a dog live with kidney failure without treatment?
Left untreated, dogs in kidney failure will die, usually within a few days to a few weeks. Death is often preceded by loss of appetite, dehydration, weight loss, vomiting, and multi-organ failure.
Can dogs recover from chronic renal failure?
There is no cure for CRF. However, if CRF is caught early and managed correctly, most dogs that experience kidney disease can go on to live a relatively normal life with some changes and long-term management.
Can chronic renal failure in dogs be reversed?
While CRF is not reversible, early treatment can provide your pet with a happier, longer, and fuller life. Regular, semi-annual checkups are key to early diagnosis and treatment of the development of chronic renal disease.
Featured Image: iStock.com/Korneeva_Kristina
WRITTEN BY
Michael Kearley, DVMVeterinarian
Dr. Michael Kearley graduated from the University of Florida College of Veterinary Medicine in 2013. He graduated with a certificate in...