dog kidney disease breathing
What Are the Symptoms of a Dog Dying From Kidney Failure?

If your dog has been diagnosed with this renal disease or you're worried they're showing signs associated with end-stage kidney failure, a lot is probably going through your mind right now. At the forefront might be which stage of kidney disease does your dog fall under, and how can you make them as comfortable as possible? It's advisable to educate yourself about what to expect as your pet's illness progresses. That way, you can give them the best quality of life all the way through their final days.
Dog Kidney Failure Stages
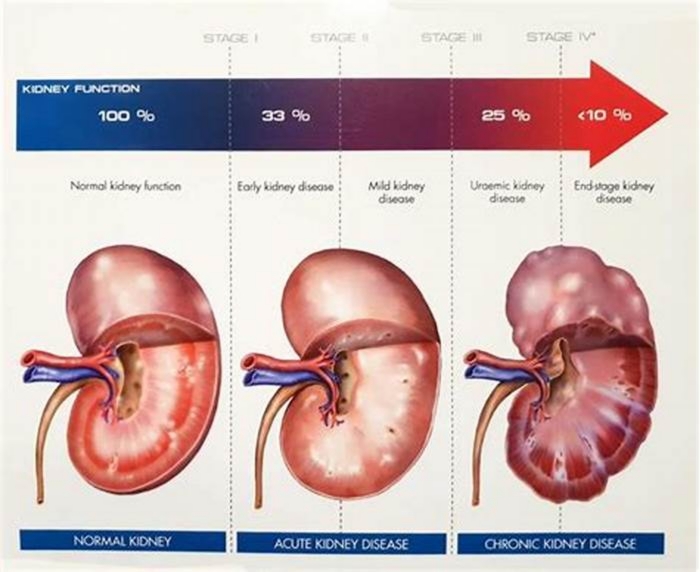
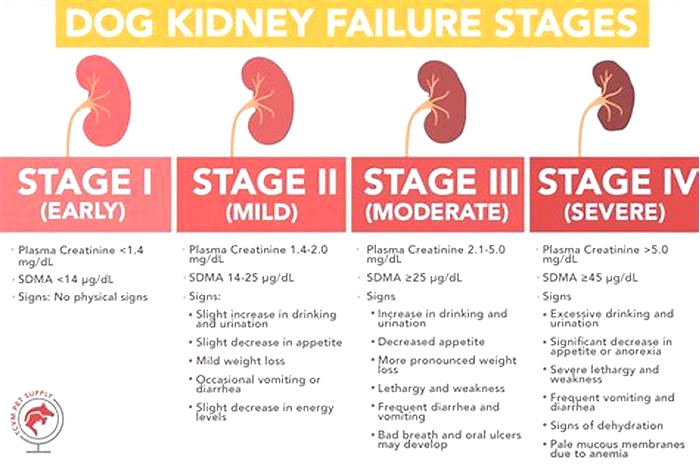
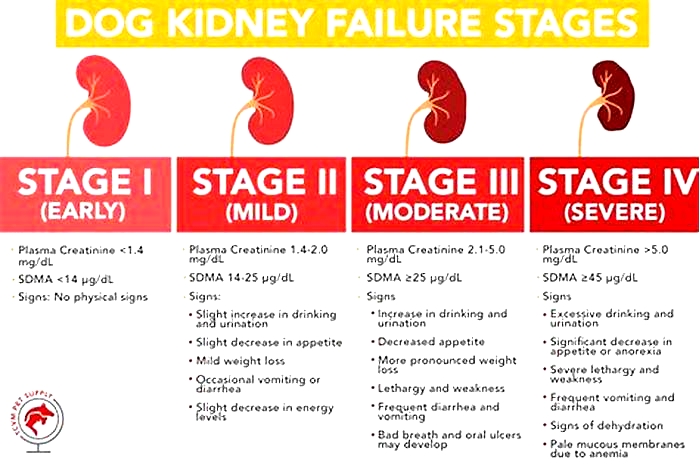
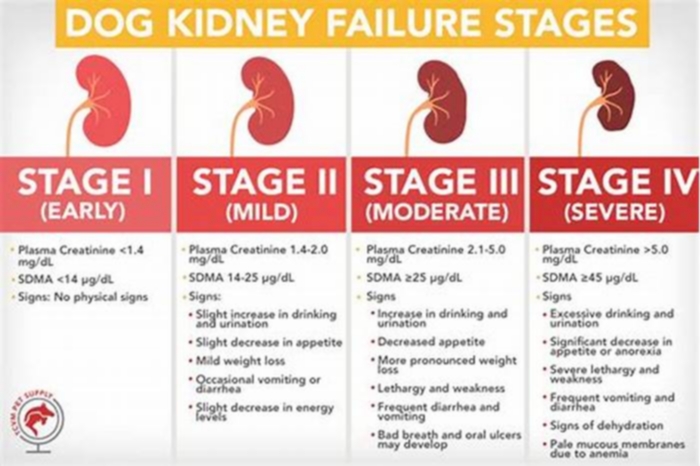
Dogs with kidney failure go through a series of four stages, from diagnosis through the eventual death of the animal. These stages do not necessarily occur within rapid succession. A dog can go through them over the course of a few months or even years. Veterinarians determine the stage your dog is in by testing the urine to look for signs of the deterioration of the kidney's functions and the blood for symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) levels.
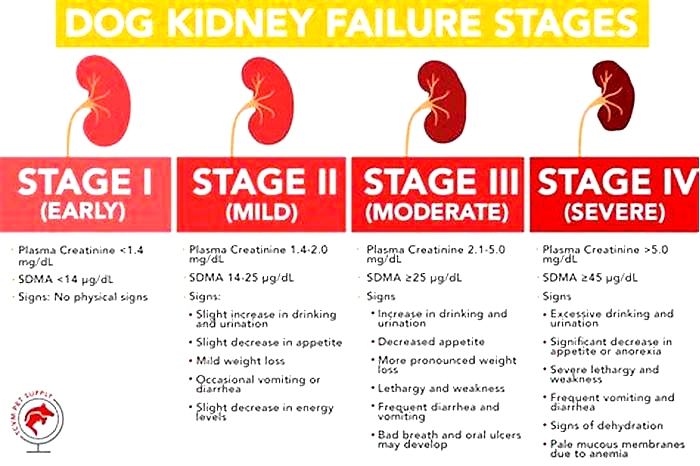
The Four Stages of Kidney Failure Chart
The canine kidney failure stages are determined by the levels of creatinine and SDMA, as well as the urine-to-protein (UPC) ratio and the animal's systolic blood pressure.
| Dog Kidney Failure Stage | Creatinine (in mg/dL) | SDMA (in g/dL) |
| Stage 1 | less than 1.4 | less than 18 |
| Stage 2 | 1.4 to 2.0 | 18 to 35 |
| Stage 3 | 2.1 to 5.0 | 36 to 54 |
| Stage 4 | greater than 5.0 | greater than 54 |
Other clinical indications that a dog is in the stages of kidney failure are:
- UPC Ratio:
- Nonproteinuric: less than 0.2
- Borderline proteinuric: 0.2 to 0.5
- Proteinuric: greater than 0.5
- Systolic blood pressure (in mmHg):
- Normotensive: less than 150
- Borderline hypertensive: 150 to 159
- Hypertensive: 160 to 179
- Severely hypertensive: greater than 180
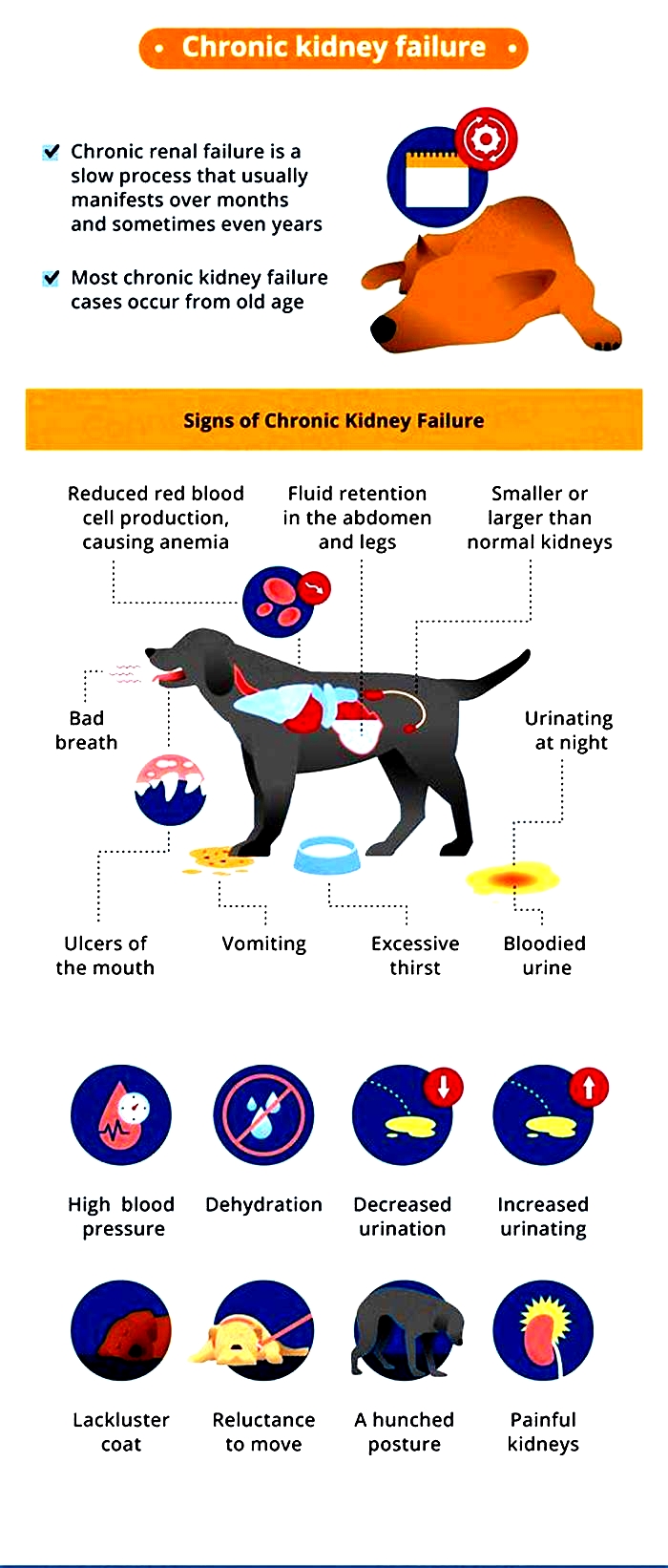
Symptoms of End-Stage Kidney Failure in Dogs
The most common signs a dog is dying from kidney failure include:
- Uremia: The buildup of waste products in the body produces a distinctive ammonia smell that is especially apparent on the breath.
- Pale, dry gums: The gums are duller and dry to the touch.
- Mouth ulcers: Uremia causes raw mouth ulcers that are painful.
- Bloodshot eyes: The whites of the eyes are bloodshot.
- Increased thirst: An affected dog drinks water excessively.
- Increased urination: The dog will urine large volumes of dilute urine.
- Dehydration: Despite more fluid intake, the dog is dehydrated.
- Decreased appetite: The dog loses interest in food.
- Weight loss: The dog steadily loses weight.
- Gradual loss of fat and muscle mass: The weight loss affects both fat and muscle mass and can cause emaciation.
- Dull coat that sheds excessively: The lackluster coat constantly sheds and looks unkempt.
- Lethargy: The dog has little energy or interest in moving around.
- Fatigue: The dog sleeps most of the day and night with only brief periods of wakefulness.
- Vomiting: The dog vomits frequently and cannot keep food down.
- Anemia: The dog may develop anemia.
- High blood pressure: The dog has elevated blood pressure.
- Incontinence: A dog cannot control their urination.
- Difficulty breathing: The dog has problems breathing normally.
- Slowing heart rate: A faster heart rate is generally present with kidney failure, but the heart rate begins to slow down during the end stage of the disease.
- Depression: The dog seems sad and does not respond to any of their favorite things.
- Low temperature: Dogs in their last days of kidney failure can experience hypothermia or a low body temperature.
- Lack of interest in surroundings: The dog is unaware of or disinterested in their surroundings.
- Disorientation: The dog acts confused at times.
- Loss of balance and coordination: The dog appears clumsy and unsteady on their feet.
- Trembling or shaking: The dog has tremors or episodes of shaking.
- Seizures: The dog suffers periodic seizures, one of the major signs of end-stage kidney failure.
Keeping Your Pet Comfortable
Watching your pet go through this can be very difficult. However, there are things you can do to help keep your dog comfortable during the final stages of kidney disease.
- Spend as much time as possible with your dog. Even being in the same room will be soothing to them.
- Make sure your dog's resting area is quiet, warm, and cozy. Provide them with their favorite blanket and toy.
- Protect your pet from other pets or people who may be too rough with them. Supervise interactions with children and teach them to be gentle with the dog.
- Pet your dog and talk to them frequently.
- Change your dog's bedding often and keep them clean and dry. Brush their fur for dry cleaning. Clean their fur with a sponge bath solution of hypoallergenic pet shampoo.
- Feed your pet a low-protein dog food appropriate for a kidney failure diet.
- If your dog refuses to eat or has trouble eating, ask the veterinarian about other feeding options such as an esophagostomy tube to keep them nourished.
- Monitor your dog's temperature and keep them warm with plenty of cozy blankets.

Last Days of a Dog Dying From Kidney Failure
While a dog owner may fear that entering the final stage of kidney failure means their dog's passing away is imminent, it is difficult to predict how long the does has left. In general, you can expect your dog to pass away within three months of moving into stage 4, though some dogs may thrive for up to a year.
It depends on the associated symptoms and other conditions that may arise due to the dog's poor health. Your dog's age is another factor. There's a lot to keep in mind, a lot to hope for, and the reality that you're facing the end of your dog's life.
Fast Fact
Controlling your dog's diet can help during their struggle with renal failure. Carefully discuss nutrition with your dog's veterinarian.
When to Consider Euthanization
When a dog enters end-stage renal failure, your veterinarian may recommend an end-of-life home treatment plan or a hospice program to make your pet's last days comfortable and maintain your pet's quality of life. For end-stage kidney failure, a treatment plan may include dialysis, a stomach tube, intravenous therapy, pain medication, and methods to care for an incontinent pet.
Depending on their symptoms, your dog may not necessarily be in severe pain, but they will be uncomfortable at the least from other symptoms, including frequent vomiting and diarrhea, lethargy and depression, and constant dehydration. Your veterinarian may recommend euthanasia if a dog is suffering, unresponsive to pain management, or too weak to handle necessary life-sustaining treatment.
Dealing With the Loss
It's hard to come to terms with the fact that a pet is dying. Find comfort in the fact that your dog appreciates your loving care in their final days. They know you love them and take comfort in your presence and all that you do to make their life easier.
2024 LoveToKnow Media. All rights reserved.
Halitosis or bad breath in dogs is a common symptom of kidney disease. High levels of urea tend to cause this bad breath to smell fishy. If your dogs breath strongly smells like ammonia, they may be suffering from kidney disease.
As kidney disease progresses into further stages in dogs, they may exhale bad breath. Toxins that build up in their gut are a common reason for this. It is a fairly common symptom and can be treated by following effective measures.
One spectacular way to fix this is for your dog to have consistent easy bowel movements so adding in some fiber, some pumpkins, etc. may help soothe things in their digestive system. The big solution to this is using probiotics. And by that, we mean using Good & Effective probiotics. Probiotics are good bacteria that help to get rid of kidney and uremic toxins. The more you give your dog, the better it is.
If youre looking for probiotics, the 2 billion to 5 billion range will not be of any help as its just not strong enough. You must get the ones with at least 25 billion or more. If youre looking to buy one, check this out!
We formulated a probiotic supplement called Kidney Restore for Cats & Dogs, which has 50 billion probiotics. Those probiotics are made up of varieties of strains that target the kidney toxins. It has other things in it that are great for the kidneys and improves kidney function for your pets.
Whatever you choose, this probiotic or one at the store, it is important to make sure that you read the nutrition facts and confirm that the probiotics are at least 25 billion or more. The ones that stores usually carry are between 2 to 5 billion and theyre just not strong enough to do the job.
If youre looking to fix that bad breath for your pet, using probiotics is a great way to solve that! Kidney Restore for Cats & Dogs is a probiotic supplement from Healthy Kidney Inc. which has had tremendous success in fixing bad breath in pets and improving many dogs kidneys.
Can Coffee Benefit Kidney Health?
Learn How Alpha Blockers Damage Kidneys
For more informational content & useful videos be sure to check out our YouTube Channel
Managing Kidney Failure in Dogs
Kidney failure in dogs can seem like a devastating diagnosis. If you've been told by your veterinarian that your dog has a kidney problem that might end in kidney failure one day, don't lose hope. Depending on the circumstances, that day may be farther off than you think. With that note in mind, here are a few things you should know.
Identifying Kidney Failure in Dogs
Kidney failure (also known as renal failure) is the end result of any one of a large number of diseases that can affect the kidneys and related organs. Technically, it occurs when the kidneys can no longer efficiently perform their function, which is to filter out toxins, maintain a normal electrolyte balance, regulate hydration, and secrete hormones needed for the production of red blood cells.
There are two broad types of kidney failure in dogs:
- Acute renal failure: When kidney function suddenly declines (in hours or days), the process is referred to as acute. Acute renal failure in dogs is most commonly associated with infections and toxins.
- Chronic renal failure: When the loss of function is more gradual (over weeks, months or years), it's called chronic renal failure. The most common cause of chronic renal failure in dogs is degeneration associated with geriatric decline. All kidneys have their own natural lifespan, but some dogs' kidneys deteriorate more quickly than others.
One of the most notable differences between acute and chronic kidney failure is that acute kidney failure is reversible if treated early and aggressively, whereas chronic kidney failure can only be managed.

The Causes of Kidney Failure
Kidney failure is ultimately caused by any disease affecting the kidneys. These include:
- Bacterial infections, like leptospirosis, which the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports can be transmitted by drinking or swimming in contaminated water. This infection can lead to inflammation of the kidneys and consequent destruction of renal cells.
- Toxicosis, or kidney poisoning, leads to damage of the kidneys' cells. It occurs when your dog ingests drugs (like ibuprofen) or poisons (like antifreeze or grapes). The ASPCA's Animal Poison Control Center lists these and other common household items that should be kept out of your dog's reach.
- Congenital disease: Inherited conditions can lead to abnormal kidney function. The Merck Veterinary Manual includes a list of these congenital diseases, from cysts to agenesis (being born without one or both kidneys).
- Geriatric degeneration: When kidneys get old, their cells can decline and die. This is, by far, the most common cause of kidney disease in dogs.
Symptoms of Kidney Failure
The most common signs of kidney failure in dogs include:
- Vomiting
- Increased drinking and urination
- Lethargy
- Weight loss
- Pale mucous membranes in the mouth and elsewhere
The severity of clinical signs associated with kidney disease can vary depending on the presentation (acute or chronic), the extent to which the loss of kidney function has progressed and the underlying cause. Your vet can determine whether these signs point to a kidney problem or another issue, like diabetes mellitus.
Treating Kidney Failure in Dogs
The treatment of kidney failure varies depending on the underlying cause and the canine patient's overall condition. Dogs that are severely ill from acute kidney failure may need hospitalization and intensive care to recover. For milder cases, antibiotics, fluids, and other medications given on an outpatient basis can prove effective. Dialysis is even a possibility for a lucky few whose pet parents can afford the high cost of treatment.
In the case of chronic renal failure in dogs, treatment generally focuses on slowing the progression of disease and improving quality of life for the patient. Treatment of anemia, blood pressure alterations, electrolyte disturbances, fluid imbalances, nausea, and appetite changes is typically necessary. Most of these signs are managed through diet changes and medication. Pets can sometimes experience a good quality of life for years after a kidney failure diagnosis.

Preventing Renal Failure
Given that chronic renal failure in dogs is most commonly the result of genetically predetermined, age-related degeneration, it's not considered preventable. Nonetheless, regular physical examinations and wellness screenings can increase your dog's chances of early diagnosis and treatment.
Acute renal failure, however, is considered preventable in many instances. Vaccination against infectious diseases, like leptospirosis, for example, can prove highly effective. Clearing households of toxins, like antifreeze; being careful with grapes and raisins; and keeping all human medications out of the reach of dogs is also important.
Understanding Your Dog's Risk
The timing of kidney degeneration is likely linked to a dog's genetics. Consequently, chronic renal failure in dogs is effectively preprogrammed to occur at a certain age. Nonetheless, no specific breed predisposition is known to exist. Certain kidney diseases that can lead to renal failure in dogs, however, can disproportionately affect specific breeds. These include the following:
- Basenji dogs are especially affected by Fanconi syndrome, which disrupts electrolyte absorption.
- Bernese mountain dogs can suffer a congenital disease of the kidneys called glomerulonephritis.
- Collies, Shetland sheepdogs and German shepherds can be affected by lupus, an autoimmune disease affecting the kidneys and other organs.
- Shar-Peis can suffer a kidney disease known as familial renal amyloidosis.
It can prove difficult to determine which dogs will suffer these conditions in advance. New blood tests, however, are now helping identify kidney disease in dogs and cats early, sometimes even many years before signs become evident. One test called the SDMA (which IDEXX notes is named for symmetric dimethylarginine, a genetic marker for kidney function) is now considered very common. Many veterinarians consider it part of their annual wellness screening; be sure to ask your vet if this test is available for your dog at your next appointment.
The Role of Nutrition
Nutrition has long been a mainstay in the management of renal failure in dogs. Since maintaining electrolyte balance and managing blood proteins are a crucial part of the kidneys' role, altering the nutrients in a dog's diet can make kidney function easier. All dog parents whose pets suffer from kidney disease should talk to their veterinarian about the ideal therapeutic diet and any additional nutritional supplements that might be in order.
Dog parents have so many more options than ever before when it comes to treating and managing renal failure. Given advances in nutrition and drugs, the longevity of veterinary renal patients is most definitely on the rise. With your veterinarian's assistance, a long life for your pup is a possibility.
Contributor Bio

Dr. Patty Khuly
Dr. Patty Khuly is an honors graduate of both Wellesley College and the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine. She received her MBA at The Wharton School of Business as part of the prestigious VMD/MBA dual-degree program. She's now the proud owner of Sunset Animal Clinic in Miami, Florida. But that's not all. Dr. K is a nerdy reader, avid knitter, hot yoga fanatic, music geek, struggling runner, and indefatigable foodie. She lives in South Miami with three dogs, countless cats, two rescued goats and a hilarious flock of hens.
You can follow her writing at DrPattyKhuly.com and at SunsetVets.com.