does kidney failure in dogs cause seizures
What Are the Symptoms of a Dog Dying From Kidney Failure?

If your dog has been diagnosed with this renal disease or you're worried they're showing signs associated with end-stage kidney failure, a lot is probably going through your mind right now. At the forefront might be which stage of kidney disease does your dog fall under, and how can you make them as comfortable as possible? It's advisable to educate yourself about what to expect as your pet's illness progresses. That way, you can give them the best quality of life all the way through their final days.
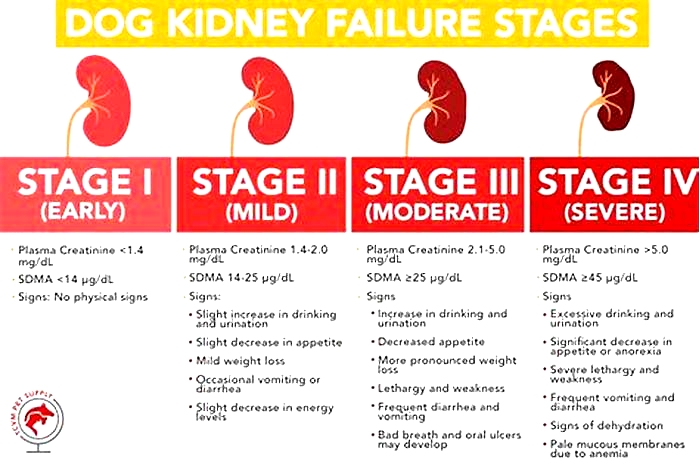
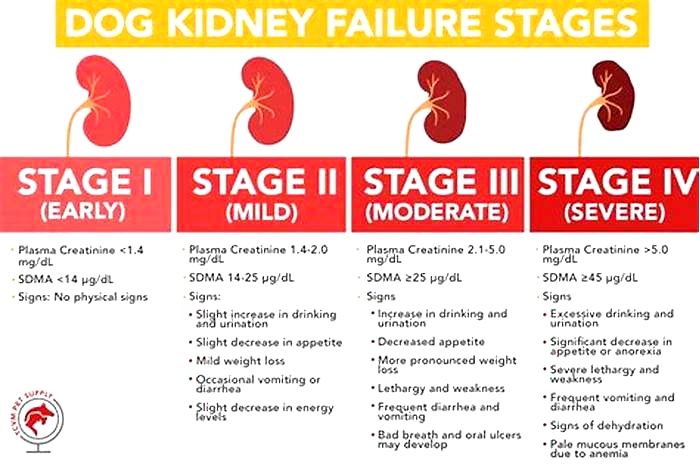
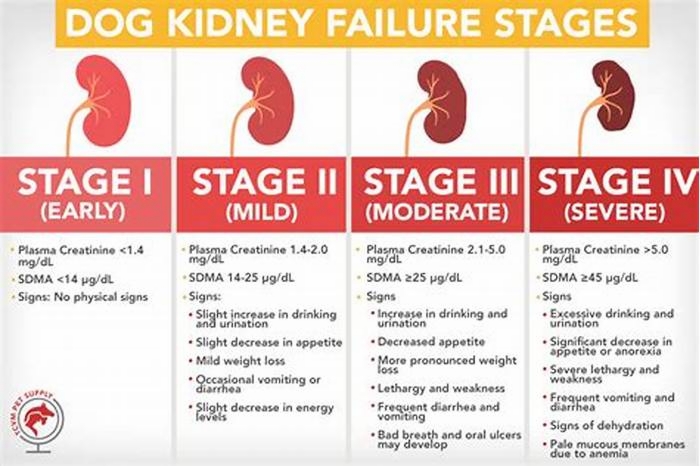
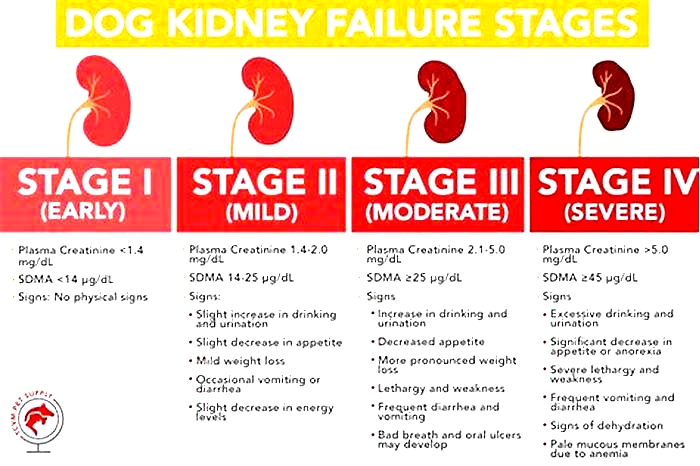
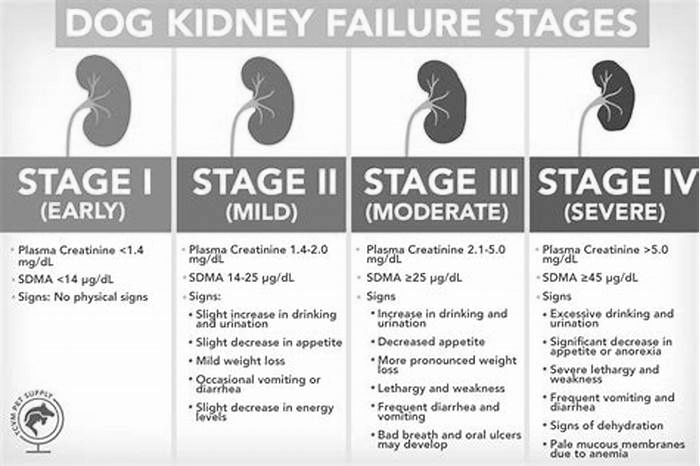
Dog Kidney Failure Stages
Dogs with kidney failure go through a series of four stages, from diagnosis through the eventual death of the animal. These stages do not necessarily occur within rapid succession. A dog can go through them over the course of a few months or even years. Veterinarians determine the stage your dog is in by testing the urine to look for signs of the deterioration of the kidney's functions and the blood for symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) levels.
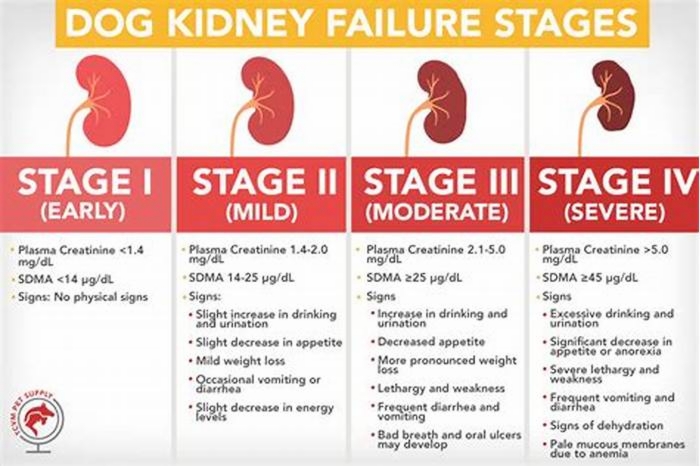
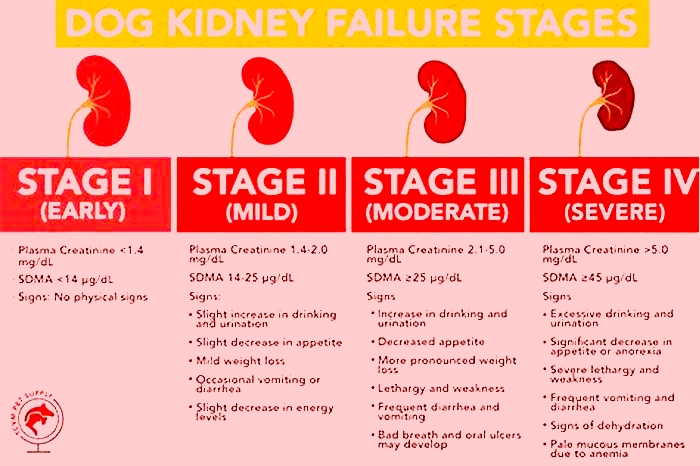
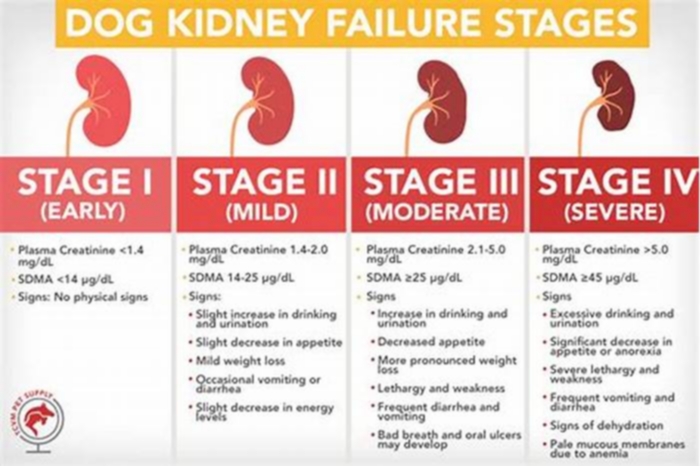
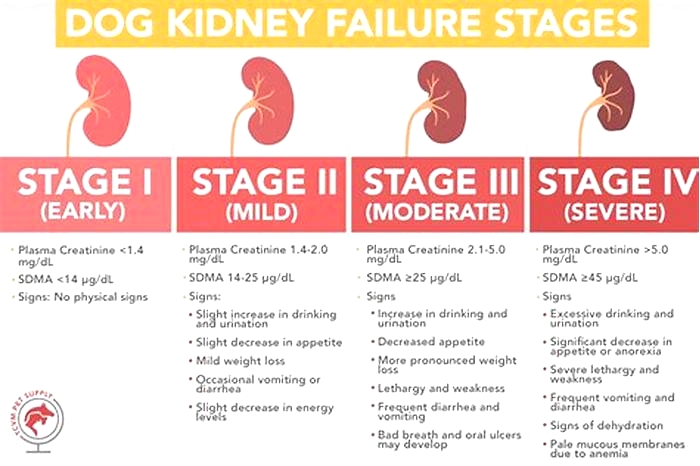
The Four Stages of Kidney Failure Chart
The canine kidney failure stages are determined by the levels of creatinine and SDMA, as well as the urine-to-protein (UPC) ratio and the animal's systolic blood pressure.
| Dog Kidney Failure Stage | Creatinine (in mg/dL) | SDMA (in g/dL) |
| Stage 1 | less than 1.4 | less than 18 |
| Stage 2 | 1.4 to 2.0 | 18 to 35 |
| Stage 3 | 2.1 to 5.0 | 36 to 54 |
| Stage 4 | greater than 5.0 | greater than 54 |
Other clinical indications that a dog is in the stages of kidney failure are:
- UPC Ratio:
- Nonproteinuric: less than 0.2
- Borderline proteinuric: 0.2 to 0.5
- Proteinuric: greater than 0.5
- Systolic blood pressure (in mmHg):
- Normotensive: less than 150
- Borderline hypertensive: 150 to 159
- Hypertensive: 160 to 179
- Severely hypertensive: greater than 180
Symptoms of End-Stage Kidney Failure in Dogs
The most common signs a dog is dying from kidney failure include:
- Uremia: The buildup of waste products in the body produces a distinctive ammonia smell that is especially apparent on the breath.
- Pale, dry gums: The gums are duller and dry to the touch.
- Mouth ulcers: Uremia causes raw mouth ulcers that are painful.
- Bloodshot eyes: The whites of the eyes are bloodshot.
- Increased thirst: An affected dog drinks water excessively.
- Increased urination: The dog will urine large volumes of dilute urine.
- Dehydration: Despite more fluid intake, the dog is dehydrated.
- Decreased appetite: The dog loses interest in food.
- Weight loss: The dog steadily loses weight.
- Gradual loss of fat and muscle mass: The weight loss affects both fat and muscle mass and can cause emaciation.
- Dull coat that sheds excessively: The lackluster coat constantly sheds and looks unkempt.
- Lethargy: The dog has little energy or interest in moving around.
- Fatigue: The dog sleeps most of the day and night with only brief periods of wakefulness.
- Vomiting: The dog vomits frequently and cannot keep food down.
- Anemia: The dog may develop anemia.
- High blood pressure: The dog has elevated blood pressure.
- Incontinence: A dog cannot control their urination.
- Difficulty breathing: The dog has problems breathing normally.
- Slowing heart rate: A faster heart rate is generally present with kidney failure, but the heart rate begins to slow down during the end stage of the disease.
- Depression: The dog seems sad and does not respond to any of their favorite things.
- Low temperature: Dogs in their last days of kidney failure can experience hypothermia or a low body temperature.
- Lack of interest in surroundings: The dog is unaware of or disinterested in their surroundings.
- Disorientation: The dog acts confused at times.
- Loss of balance and coordination: The dog appears clumsy and unsteady on their feet.
- Trembling or shaking: The dog has tremors or episodes of shaking.
- Seizures: The dog suffers periodic seizures, one of the major signs of end-stage kidney failure.
Keeping Your Pet Comfortable
Watching your pet go through this can be very difficult. However, there are things you can do to help keep your dog comfortable during the final stages of kidney disease.
- Spend as much time as possible with your dog. Even being in the same room will be soothing to them.
- Make sure your dog's resting area is quiet, warm, and cozy. Provide them with their favorite blanket and toy.
- Protect your pet from other pets or people who may be too rough with them. Supervise interactions with children and teach them to be gentle with the dog.
- Pet your dog and talk to them frequently.
- Change your dog's bedding often and keep them clean and dry. Brush their fur for dry cleaning. Clean their fur with a sponge bath solution of hypoallergenic pet shampoo.
- Feed your pet a low-protein dog food appropriate for a kidney failure diet.
- If your dog refuses to eat or has trouble eating, ask the veterinarian about other feeding options such as an esophagostomy tube to keep them nourished.
- Monitor your dog's temperature and keep them warm with plenty of cozy blankets.

Last Days of a Dog Dying From Kidney Failure
While a dog owner may fear that entering the final stage of kidney failure means their dog's passing away is imminent, it is difficult to predict how long the does has left. In general, you can expect your dog to pass away within three months of moving into stage 4, though some dogs may thrive for up to a year.
It depends on the associated symptoms and other conditions that may arise due to the dog's poor health. Your dog's age is another factor. There's a lot to keep in mind, a lot to hope for, and the reality that you're facing the end of your dog's life.
Fast Fact
Controlling your dog's diet can help during their struggle with renal failure. Carefully discuss nutrition with your dog's veterinarian.
When to Consider Euthanization
When a dog enters end-stage renal failure, your veterinarian may recommend an end-of-life home treatment plan or a hospice program to make your pet's last days comfortable and maintain your pet's quality of life. For end-stage kidney failure, a treatment plan may include dialysis, a stomach tube, intravenous therapy, pain medication, and methods to care for an incontinent pet.
Depending on their symptoms, your dog may not necessarily be in severe pain, but they will be uncomfortable at the least from other symptoms, including frequent vomiting and diarrhea, lethargy and depression, and constant dehydration. Your veterinarian may recommend euthanasia if a dog is suffering, unresponsive to pain management, or too weak to handle necessary life-sustaining treatment.
Dealing With the Loss
It's hard to come to terms with the fact that a pet is dying. Find comfort in the fact that your dog appreciates your loving care in their final days. They know you love them and take comfort in your presence and all that you do to make their life easier.
2024 LoveToKnow Media. All rights reserved.
Kidney Failure in Dogs: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
In this post, well dive into the causes of kidney failure in dogs, common symptoms you should look out for, available treatment options, and more.
Table of Contents
Pro Tip: Not all pet insurance will cover your vet bills if your dog develops a long-term illness. Thats why its very important to have the right pet insurance plan in place.
Types of kidney failure in dogs
Just like in humans, healthy kidneys in dogs control blood pressure, regulate hydration, remove toxins, release hormones needed to produce red blood cells, and maintain a normal electrolyte balance. If the kidney function is impaired, kidney failure occurs. When the kidneys dont work properly, a number of other organs can be affected, including the brain and heart.
Kidney failure (also called renal failure) in dogs can be chronic or acute:
Chronic kidney failure
This occurs when the kidneys lose function gradually and is typically caused by degeneration related to old age. Chronic kidney failure is the most common type of kidney disease in dogs, occurring in 0.5% to 1% of dogs.
Acute kidney failure
This occurs when a canine's kidney function suddenly decreases, usually within hours or a few days. Its typically caused by a severe kidney infection or the consumption of toxins.
The main difference between these two types of kidney failure is that acute kidney failure can be reversed with timely and aggressive treatment. Chronic kidney failure, on the other hand, cant be reversed or cured and it can only be managed. In most cases, the damage to the kidneys has been happening for more than three months and the kidneys will continue to worsen.
What causes kidney failure in dogs?
Chronic kidney failure in dogs
The exact cause of chronic kidney failure is often difficult to pinpoint because of its slow onset. Early symptoms are usually mild and can be easily overlooked or dismissed.
Dental disease is a leading cause of chronic renal failure in senior dogs. Bacteria build up in the animals teeth and enter the digestive system through eating and drinking, affecting the kidneys ability to filter waste over time.
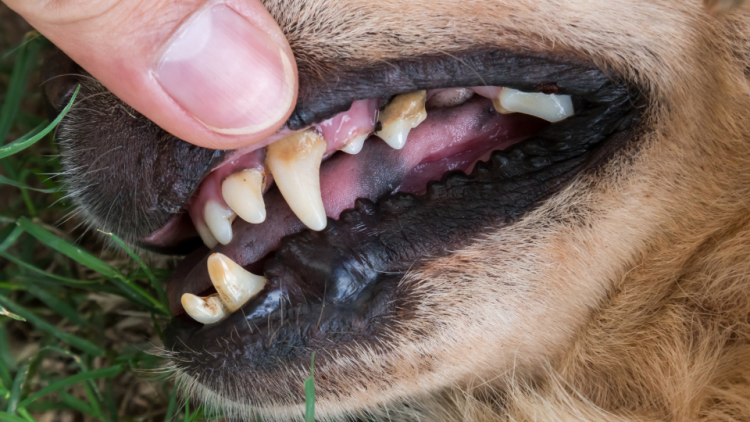
Chronic kidney failure can also be caused by:
- Congenital diseases or birth defects (such as agenesis, when the dog is born missing one or both kidneys)
- Kidney cancer (renal neoplasia)
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Kidney infections
- Fanconi syndrome
- Elevated calcium (hypercalcemia)
- Kidney stones
- Renal dysplasia
- Immune system dysfunction
- Poor blood flow to the kidneys
- Blocked urine movement or flow
- Certain medications (such as NSAIDs and some antibiotics)
Acute renal failure can also lead to chronic renal failure.
Acute kidney failure in dogs
Acute renal failure is most often a result of a dog ingesting poison. It might be antifreeze, household cleaners, or certain drugs. Some human foods like grapes and raisins have also been known to cause kidney failure if eaten frequently and in larger quantities.
Severe bacterial infections can also cause acute kidney failure. Even though kidney infections can occur spontaneously, theres usually a reason why the dog has trouble fighting off the infection, such as urine blockage or kidney stones.
Leptospirosis is one example of a bacterial infection that can cause sudden renal failure in pups. Our canine companions can get leptospirosis by coming into contact with infected urine, water, soil, water, food or bedding, or through a bite from an infected animal. Be sure to talk to your vet about vaccinating against this disease.
Kidney issues can also result from decreased blood flow through the kidneys. This can be caused by severe dehydration (usually from severe diarrhea or vomiting), heatstroke, or snake bites, and bee stings.
Signs of kidney failure in dogs
The most common symptoms in dogs with kidney failure include:
- Excessive thirst and urination
- Lethargy
- Decreased appetite
- Weight loss
- Bad breath
- Pale gums
- Vomiting
- Blood in urine
- Ulcers in the mouth
- Uncoordinated movement such as stumbling
- Intestinal seizures
Dogs with chronic renal failure might not show any clinical signs at first, or the signs might be very subtle.
In severe renal failure, the amount of urine might actually decrease, or the dog might stop making urine altogether. As the condition worsens, other symptoms may include blood in the stool, black or tarry stool, or vomiting blood.
Diagnosing kidney failure in dogs
Blood and urine tests are commonly performed to diagnose kidney failure. Other tests, such as ultrasound, X-rays, and special blood tests might be needed in order to assess the severity of the disease and determine the cause for the failure. In some cases, a biopsy of the kidney might be recommended.
How to treat kidney failure in dogs
Treatment for kidney failure in dogs will depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying reason that caused their kidney to fail.
Dogs with acute renal failure can get very ill and might need to be hospitalized. Milder cases can be treated with antibiotics and fluids on an outpatient basis.
In some cases, dialysis might be necessary. Signs that indicate dialysis should be considered include very high potassium levels, lack of improvement in lab results while the pet receives intravenous fluids, and fluid in the lungs. Both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis can be effective but are generally quite expensive.
While damage from acute renal failure is more easily treated, chronic renal failure will cause irreversible damage to your dogs kidneys unless caught early. For that reason, veterinarians generally focus on slowing down the progression of the disease and finding ways to improve the dogs quality of life, usually with medication and diet changes.
Your pups treatment plan might also include:
- Electrolytes to balance out blood levels
- Medications that encourage the production of urine
- Medications to ease gastrointestinal problems
- Medications to reduce vomiting
- Medications for anemia
- Blood pressure management
If kidney disease is left untreated, end-stage renal failure might occur, leading to death. If you suspect your pet has kidney failure, contact your veterinarian or take your dog to an emergency clinic for a diagnosis and treatment.

Cost to treat dogs kidney failure
The cost of diagnosis and treatment will also depend on the cause, as well as on how the dog responds. Initial diagnostic tests usually range between $200 and $750, whereas long-term management of chronic kidney failure can cost between $100 and $500 per month, depending on the prescribed medications and how often IV fluid therapy is required.
Pro Tip: Every dog owner should consider pet insurance. Even if you believe you have enough money to cover veterinary costs, pet insurance could still save you thousands of dollars if your dog gets sick or injured.
Whats the prognosis?
Kidney failure is a very serious disease and about 60% of pets suffering from it will either die or be euthanized because of it. In cases when medical treatment has failed, the chance of survival without dialysis is extremely low. About half of the patients that receive dialysis will recover, depending on what caused the failure. Many of them will recover only partially and end up with permanent kidney damage.
However, some pups manage to recover completely and have a good quality of life for years after being diagnosed with the disease.
Talk to your vet about what you should expect after your dog has been diagnosed and treated for kidney failure. The vet might recommend nutritional supplements and/or a therapeutic diet to manage your pups condition.
Preventing kidney failure in dogs
Considering the fact that acute renal failure is usually caused by ingesting toxins or foods like raisins, preventing it is fairly easy. Make sure to get any poisons, medications, and dog-unsafe foods out of your pups reach. You can also get your dog vaccinated for Leptospirosis.
Chronic renal failure is usually age-related and genetically predetermined, so theres not much you can do to prevent it. However, taking your pet for annual wellness checkups and physical exams can increase the chances of catching the disease early and start treatment before it progresses and becomes more serious.